Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
NEUROGENIC AND VASCULAR CLAUDICATION
VASCULAR PAIN
- Vascular claudication – lower extremity pain secondary to arterial insufficiency.
- It occurs in patients with peripheral arterial diseases ,eg ; atherosclerosis.
- There is a mismatch between the oxygen demand and the oxygen supply in the lower extremity.
- Pain starts distally within the calf and the leg and radiates proximal especially during walking as there is not enough blood supply going distally.
- It will be affected by muscle function such as walking or riding a bicycle.
- Changes in the lower extremity may also be present as an ulcer, edema, or skin changes in the form of shiny, hairless, dystrophic skin.
SPINE PAIN
- Neurogenic claudication- narrowing of the spinal canal and the spinal foramen. The pain radiates from proximal to distal.
- In neurogenic claudication which is heaviness and cramps of the calves the patient will walk a certain distance and then get the pain.
- Symptoms relieved by leaning forward or sitting down.
- Leaning over while riding a bicycle will relieve the symptoms.
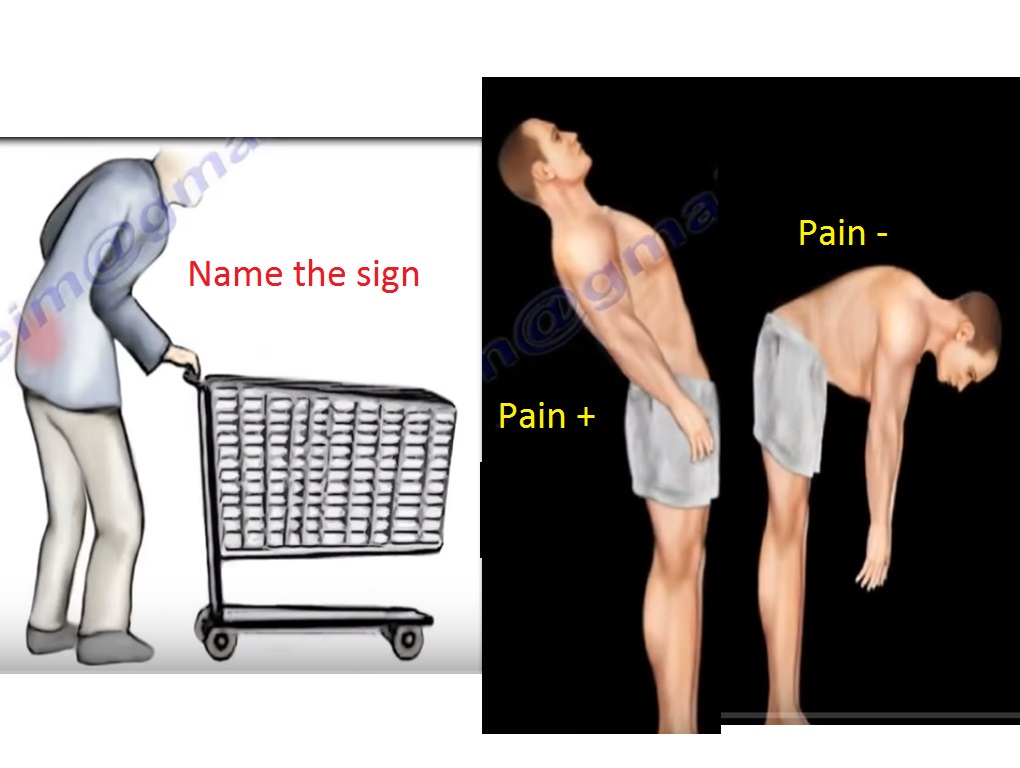
- Shopping cart sign- leaning over the shopping cart will relieve the spine pain but not helpful in vascular pain.
- Flexion increases the size of the neural foramen and will increase the space for the thecal sac.
- Examination of the patient with lumbar spinal stenosis should include evaluation of the peripheral pulses and the evaluation for decreased asymmetric or absent pulses.
- Examination of the pulses on both feet should be done routinely. Pulses are normal in neurogenic claudication.
WHAT IS THE CLINICAL PICTURE OF SOMEBODY WITH VASCULAR AND NEUROGENIC CLAUDICATION?
- An elderly woman with difficulty in ambulating more than one block. She will have cramps in her leg and leg feels heavy. After 100 feet she has to sit down. Her feet will burn at night and her calves hurt more than her thigh.
- Clearly this is a picture of somebody with vascular claudication.
- She is able to shop for groceries but she must lean forward on the shopping cart to ease her pain and has no weakness or numbness on examination. So she also has neurogenic claudication.
- When we get the MRI we see a moderate stenosis at L4- L5 and L5 -S1.
- X rays show calcification in aorta.
- She needs a vascular workout because her pain is distal in her legs and because of burning in her feet and x-ray showing calcification of the aorta.
- Distinguishing between neurogenic claudication and vascular claudication is important because the management is different and because both may occur together and the treatment may be more complicated.
- When you look at the X-ray of the Lumbosacral area to assess the spine, check for calcification in the aorta and order an ankle brachial index (A.B.I).
Leave a Reply