Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
ANATOMICAL AND SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE SUBSCAPULARIS MUSCLE
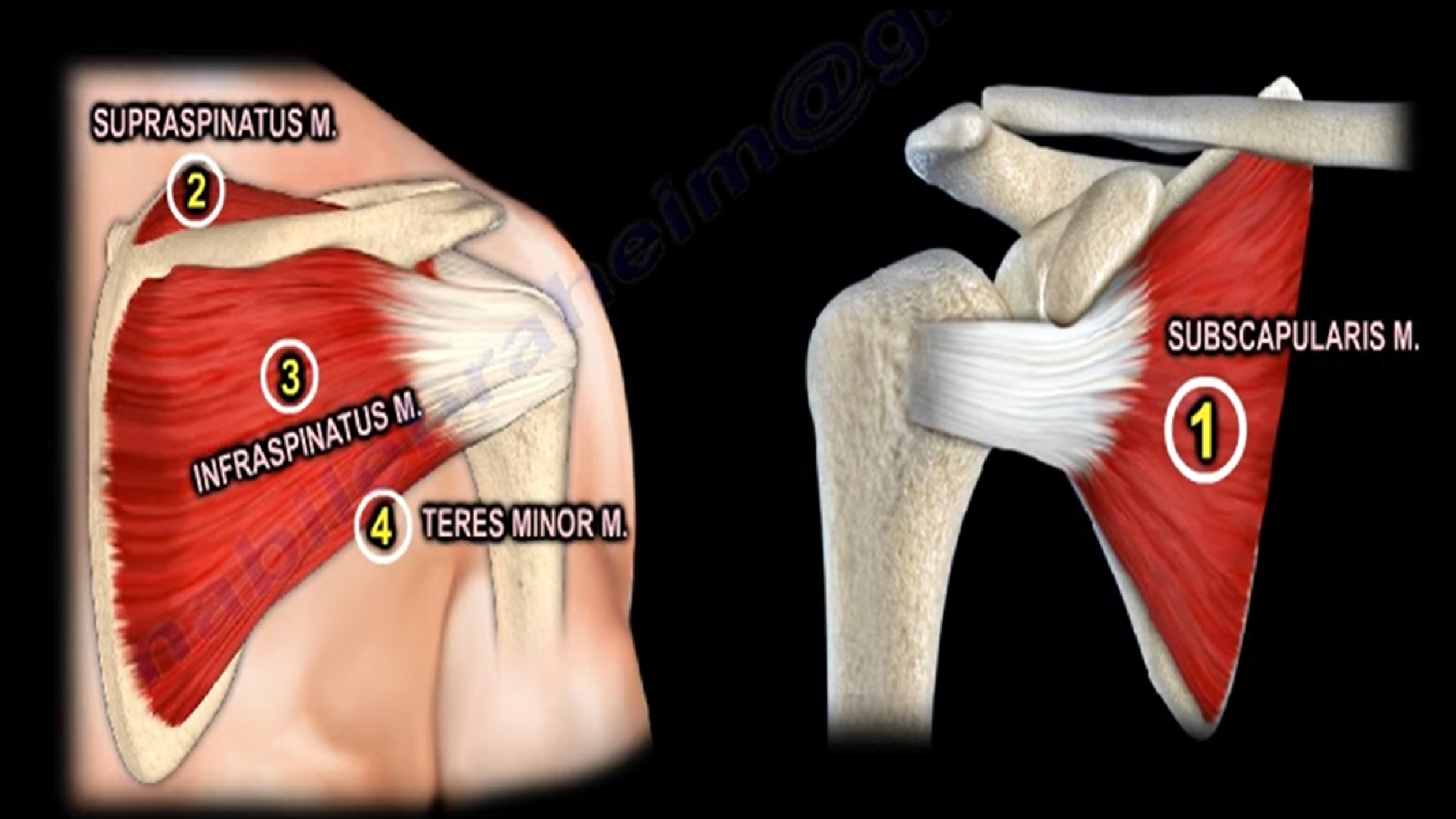
The subscapularis muscle is a large muscle that originates on the anterior surface of the scapula and lies in front of the shoulder.
- Origin- Subscapular Fossa of the scapula.
- The muscle passes to its insertion into the lesser tuberosity underneath the arch formed by the cracked process and the combined origins of the coracobrachialis muscle and the short head of the biceps.
- It is the largest of the 4 rotator cuff muscles and it provides about 50% of the total cuff strength.
- It inserts into the lesser tuberosity of the humerus, while the other rotator cuff muscles insert into the greater tuberosity.
What is the innervation of the subscapularis muscle?(What is the nerve supply of the subscapularis?)
- The subscapularis muscle is supplied by the upper and lower subscapular nerves which comes from the posterior cord of brachial plexus.
Blood supply of subscapularis?
- The subscapular artery, largest branch of the axillary artery.
Axillary Nerve and its relationship to the subscapularis?
- The axillary nerve branches of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus passes over the subscapularis muscle and then curves backwards below it and underneath the shoulder joint capsule to enter the quadrangular space with the posterior humeral circumflex artery.
What is the function of the subscapularis muscle?
- It acts as a dynamic stabilizer of the humeral head and aids in lifting across the chest. The main function of the subscapularis muscle is to adjust and rotate the arm medially or internally.
- Testing the integrity of the subscapularis muscle and tendon, focusing on manual examination that tests the function of internal rotation of the subscapularis muscle.
- At the insertion of the subscapularis tendon into the lesser tuberosity lies the transverse humeral ligament. The long head of the biceps tendon lies within the bicipital groove and is held in place by the transverse humeral ligament. When a complete rupture of the subscapularis tendon occurs, the transverse humeral ligament may also become torn causing medial dislocation of the biceps tendon from the bicipital groove. Consider subscapularis tear when you see subluxation of the biceps medically.
Mechanism of subscapularis tendon tear:
- It is usually an acute aversion in younger patients with a fall into an outstreched arm with hyperabduction and external rotation.
- The presentation is usually anterior shoulder pain following a forcible external rotation injury to the shoulder.
- The injury can be iatrogenic due to failure of repair of the subscapularis tendon after open procedures.
How does the tear present itself?
- There may be an avulsion of the lesser tuberosity of the humerus. The subscapularis tear may be isolated or may be associated with other rotator cuff tears.
- 88% of patients with medial biceps tendon subluxation are found to have subscapular tendon tear.
Diagnosis of Subscapularis Rupture:
- Tears are not uncommon and can be missed.
- Can be either acute tear or chronic tear.
- Can also be partial or complete.
What are the clinical signs of Subscapularis Tendon Injury?
- Anterior shoulder pain.
- Anterior shoulder swelling.
- Decreased ROM.
- Weakness of internal rotation.
- Increased external rotation of the shoulder compared to the other shoulder.
What are the Clinical tests for Subscapularis Tendon Rupture:
- Lift-off Test
- Bear-Hug Test
- Belly Press Test
All these tests show weakness of internal rotation of the shoulder.
What is Lift-Off Test : (Gerber’s Lift-Off test)
- The patient places the hand behind their back at the lumbar level and lifts the hand away from the back when the patient has an intact subscapularis tendon.
- The strength and the power to do these maneuvers can be tested by the examiner’s hand to resist this maneuver and compare it to the other side.
- If the patient is unable to lift the hand off of the lower back, then a tear of the subscapularis tendon is suspected.
- The examiner will hold the patient’s hand away from the back at the lumbar region and let go
- Patient will be unable to keep the hand away from the back if the subscapularis tendon is torn.
What is Belly-Press Test? (Napoleon Sign)
- The patient presses the palm of the hand against the abdomen with the wrist in a neutral position. This is an example of an intact subscapularis tendon. A positive sign for the belly-press test occurs if the patient is unable to press his belly without wrist volar flexion or the elbow falling posteriorly.
- The “Bear-Hug” Test is a test used to examine for a possible tear of the subscapularis tendon,especially the upper part of the subscapularis.
How do you do the Bear-Hug Test?
- The patient is asked to place the palm of the hand onto the opposite shoulder with the elbow anterior to the body.
- The patient will maintain the internal rotation of the shoulder in this position and the examiner will then attempt to externally rotate the arm.
- A positive test will result when the patient weakness of the arm compared to the other arm.
Radiological Examination :
- Tears of the subscapular tendon may be diagnosed by using MRI or ultrasound.
- The MRI will show detachment of the subscapularis from its insertion into the lesser tuberosity of the humerus.
- The Sagittal MRI will also show you if there is an atrophy the muscle.
- If the patient has a total shoulder replacement, and the patient fell down and there is an increase in the passive external rotation of the shoulder, the X-ray will be probably be normal and then you will probably need to do an ultrasound evaluation of the shoulder to check the integrity of the subscapularis tendon.
Ultrasound Examination :
- Ultrasound imaging of the subscapilar tendon is easy.
- The probe is placed transversely over the bicipital groove to identify the groove and the biceps tendon while the arm is in a neutral
position. - The arm is then externally rotated view the subscapularis tendon.
Tears of the Subscapularis Tendon :
Treatment :
1)Complete Tear :
- Surgical Repair
- Repair may be either open or arthroscopic.
- Biceps tenodesis during the repair is associated with improved outcome.
- Biceps tenodesis is usually done if the biceps is involved in the process, otherwise subluxation of the biceps will stress and fail
the repair - Subscapularis tears may be missed.
- It can be a hard diagnosis and if it is missed, the patient will have major disability.
- The condition becomes chronic with the treatment becoming harder and it may require pectoralis major transfer for reconstruction. This will improve the function and decrease the pain.
- The subcoracoid position of the transfer allows redirection of the pectoralis major into a direction that is recreating the vector of the subscapularis tendon.
2) Chronic Muscle Tear:
- Pectoralis major muscle transfer is the procedure of choice.
- Arthroscopic identification of a chronic subscapularis tear can be done by the comma sign, which represents avulsion of the superior glenohumeral ligament.
What is the landmark for appropriate placement of the anchor for the upper border subscapularis repair?
•The superior glenohumeral ligament.
•If the patient has a chronic supraspinatus and infraspinatus tear and the patient is young, and the tear cannot be repaired, then
you probably will need to do latissimus Dorsi transfer.
- Preoperative subscapularis function is necessary for a good clinical outcome from that transfer.
- Examine the patient clinically, check the lift off test and the abdominal compression test.
- You need to show that patient has a good subscapularis muscle function before you do the Latissimus dorsi transfer and confirm this with an MRI.
Why is the subscapularis tendon important in posterior dislocation of the humeral head?
- Posterior dislocation of the humeral head with a reverse Hill-Sachs lesion is a rare condition.
- The condition can be repaired after reduction of the dislocation with the Mclaughlin procedure utilizing the subscapularis tendon if the lesion is between 20-40% of the humeral head.
- The subscapularis tendon is used to fill the reverse Hill-Sachs lesion using suture anchors. The screws can also be inserted into a portion of the lesser tuberosity that is attached to the subscapularis.
Leave a Reply