Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Shoulder dislocation refers to dislocation of Glenohumeral joint.
It is the most commonly dislocated joint in the human body.
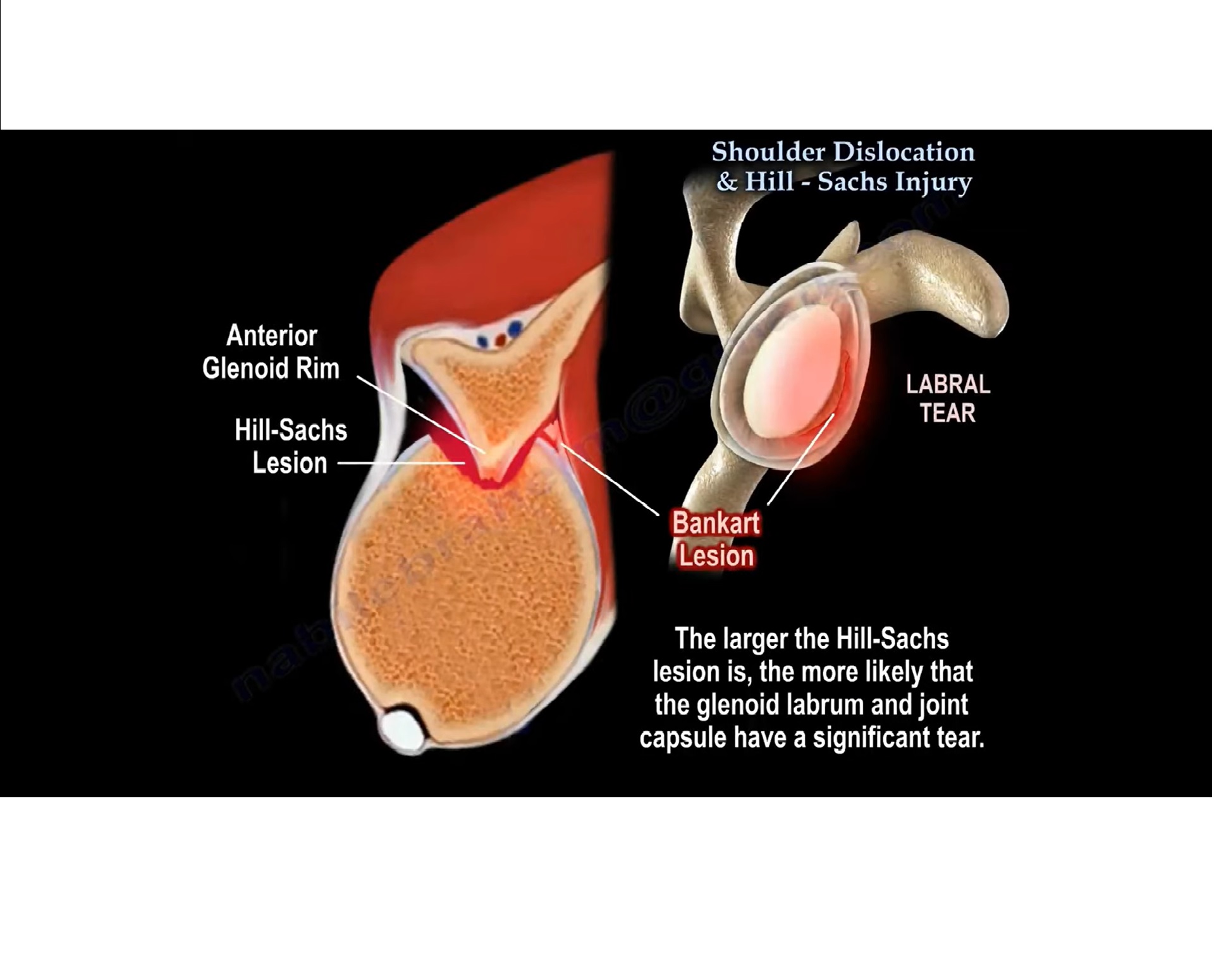
Eg: When shoulder dislocates anteriorly –the anteroinferior part of the labrum gets injured-BANKART LESION
- The labrum reinforces the glenoid cavity and acts like a guard between the joint capsule and shoulder joint .
- The axillary nerve is the most commonly injured nerve during the shoulder dislocation.
- Injury to the axillary nerve results in numbness and parasthesia around the shoulder joint-REGIMENTAL BADGE SIGN
and weakness during abduction of the shoulder joint. - Elderly patient+ weakness in abduction of shoulder joint = rotator cuff tear
Young patient + weakness in abduction of shoulder joint= axillary nerve palsy.
Types of Shoulder Dislocation
• Anterior dislocation ( most common type about 95%)
• Posterior dislocation ( rare type about 5%)
Anterior Dislocation
- Mechanism of Injury: Indirect force acting on the shoulder joint with a combination of abduction ,extension and external rotation.
(the arm will be positioned away from the body with backward rotation.) - Injuries associated with Anterior Dislocation :
• Bankart lesion – Tear of the anteroinferior part of labrum .
It is associated with a high recurrence rate of dislocation in young patients
- It can be of 2 types –fibrous /bony
• Greater tuberosity fracture
• Hill-Sachs lesion- The head of humerus may get impacted against antero-inferior edge of glenoid cavity
causing an indentation on the head of humerus called Hill Sachs lesion
Treatment
• Immediate reduction followed by Immobilisation of shoulder joint – Usually for 7-10 days.
• Surgery is the mode of treatment in patients with recurrent shoulder dislocations.
Posterior Dislocation
- Mechanism of Injury: Associated with high voltage electric shock ,seizures and it is often missed on X-rays
( The shoulder gets locked in internal rotation and there will be lack of external rotation of shoulder when compared to the normal side)
Injuries associated with posterior dislocation
• Reverse Bankart lesion
• Lesser tuberosity fracture humerus
• Reverse Hill-Sachs lesion.
Axillary view of shoulder joint is the best to diagnose posterior dislocation.
Leave a Reply