Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Proximal humerus fracture
- 70 % occur in female
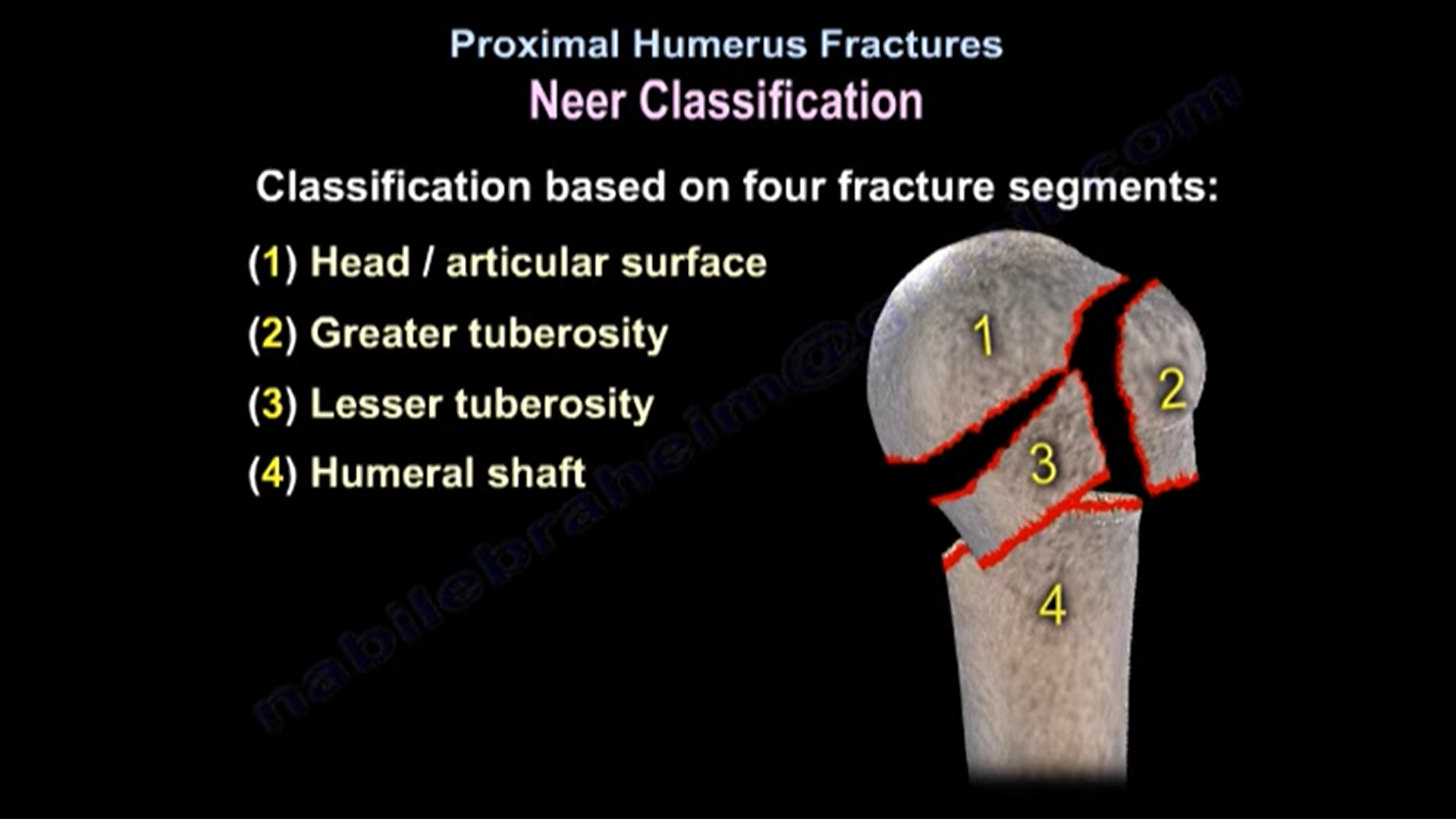
NEER Classification
Based on 4 fracture segments
1) Head/ articular surface
2) Greater tuberosity
3) Lesser tuberosity
4) Humeral shaft
-To assess the position of humerus head: xray Ap- Scapular Y view / axillary view
Treatment depends on Age
- No. Of fracture parts
- Fracture displacement
Greater tuberosity fracture
- Rotator cuff retract the fragment superiorly and posteriorly.
- If displacement is >5mm Or > 3mm( in young ) fixation should be done
- Need of surgery is to avoid malunion, impingement, mechanical block, altered shoulder mechanics.
2 part surgical neck fracture
- Shaft moves forward and medially by pectoralis major muscle
Treatment
Conservative treatment-
1) Brief immobilization
2) Pendulum exercise
3) Elbow ROM
- Good outcome will occur after initiation of physiotherapy and passive motion within 2 weeks of injury.
- Immobilization > 3 weeks lead to stiffness of shoulder
If unstable and displaced fracture
In young individual – ORIF
Old individual- Fixation/Prosthesis/conservative
If > 65 year old, no difference between functional outcome of operative and non operative treatment.
- In the operative group, high risk for reoperation and low risk of non union
- majority of non union occur at surgical neck
Head shaft angle – line over diaphyseal axis and line perpendicular to anatomic neck segment plane.
– If angle > 90° & Head shaft translation< 50% — good prognosis
– If angle 50%– bad prognosis, surgical treatment needed
SURGERY
1) Locked plate technique – In younger individual with displaced humerus fracture
- Plating restore the medial cortical support
- Advantage is reduced fixation failure
- complications: Screw cutout, penetration of articular surface
- Deltopectoral approach ( put the plate lateral to bicipital groove) – To preserve axillary nerve
Blood supply of the proximal humerus -anterior humeral circumflex artery and it’s ascending branch with it’s terminal branch
– blood supply depends on the metaphyseal extension to humeral head
– If the extension >8-9mm, medial hinge is not displaced, or valgus impacted fracture – indicates blood supply is present
2) Arthroplasty
Indications
– In older age
– In head splitting fracture
– In displaced 4- part fracture
– Poor bone quality
– Varus malalignment
- Arthroplasty has better outcome if prosthesis done acutely.
- Hemi arthroplasty produces a reliable pain relief and unreliable function, which has to do with the difficulty in reconstruction of the Tuberosities to restore the rotator cuff function .
- To restore the retroversion (~25°) keep the forearm in flexed elbow position.
- Restore the head height by measuring from top of the head to the superior border of pectoralis major(approx~ 5.6 CM)
- Repair of the tuberosity is mandatory otherwise there will be non union and restriction of overhead motion and rotation.
- Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty is indicated in fractures, cuff,or the Tuberosities are unreconstructable in elderly.
- Healing of greater tuberosity in reverse arthroplasty lead to increase in external rotation.
Leave a Reply