Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Radial nerve can be identified as it runs through the spiral groove between the heads of triceps. The nerve lies posterior to the deltoid tuberosity. The nerve crosses the posterior aspect of the humerus about 20 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle and about 15cm proximal to the lateral epicondyle. When there is a fracture, the anatomy becomes distorted because of the fracture, so a different method is reliable. The radial nerve can be found 4cm proximal to the point of confluence of the triceps aponeurosis and the long and lateral head of the triceps. The radial nerve enters the anterior compartment of the arm approximately 10 cm proximal to the elbow joint.
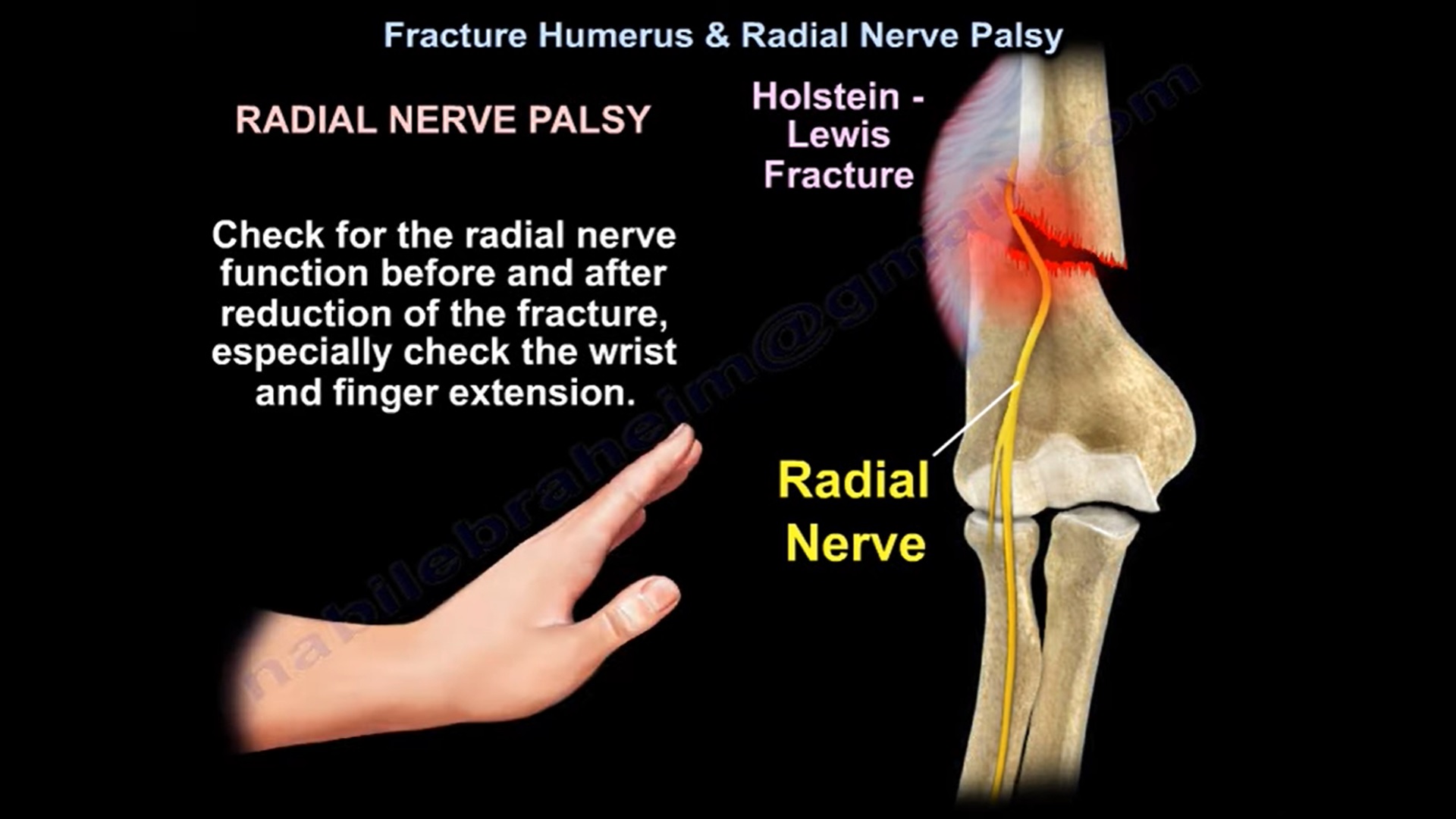
Radial nerve palsy is about 8-15% in patients with humeral shaft fractures. It is usually neuropraxia. Always check for radial nerve function .
In Holstein Lewis fracture, which is a spiral fracture of the distal third of the humerus , the neuropraxia of the radial nerve is approximately 22% . Check for the radial nerve function before and after reduction of fracture, especially check the wrist and finger extension. The primary radial nerve palsy usually occurs from the injury with an increase incidence with the distal third holstein lewis fracture and in midshaft transverse fracture. In closed fracture, usually there is a neuropraxia of the radial nerve that will improve with time with open fracture , consider that there is a laceration of the radial nerve ( neurotmesis) .
In open fractures, there will be high incidence of partial or complete laceration of radial nerve therefore consider the exploration of the nerve .
If the fracture is closed with complete radial nerve palsy , usually the treatment is coaptation splint followed by a functional brace and observation for the return of radial nerve function. 85% patients will show improvement in about 3-4 months and full recovery at 6 months.
In open fracture, there is an absolute indication to explore the radial nerve with nerve repair, delayed nerve graft or tendon transfer. If the open fracture is associated with radial nerve palsy, then you do exploration of the open wound , you explore the radial nerve and you fix the fracture. Patient with radial nerve palsy usually present with weakness of wrist and finger extension.
Weakness of wrist extension and finger extension.
Make sure that the patient extend their metacarpophalangeal joint and not their interphalangeal joint. The interphalangeal joint extension is the function of the intrinsic muscles supplied by ulnar nerve and bot by radial nerve.
If you are not sure ask the patient to hitchhike .its a better test. When you check for recovery of wrist extension, eliminate gravity to be able to check the 2/5 recovery .Against gravity it will be 3/5 and this is the way to check extension of wrist with gravity eliminated.
How do you observe for nerve recovery?
immobilise the fracture ,then splint the wrist and obtain EMG and nerve studies in about 6 weeks. The result is such that fibrillation is bad and polyphasic is good
Monitor brachioradialis muscle because it is the first muscle to recover. The extensor indices muscle is the last one to recover .measure the distance from the fracture down to brachioradialis ,which is the first muscle to be reinnervated .This may give you the estimated time which is needed for brachioradialis to get some innervation. The nerve will recover 1 mm/day . Wrist extension with radial deviation recovers first because the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis gets innervated first before the extensor carpi ulnaris .Then you will explore the nerve if the nerve fails to recover within 4-6 months (patient may need tendon transfer).
What do you transfer? – To get wrist extension, you transfer the pronator teres to extensor carpi radialis brevis. for finger extension you can transfer the flexor digitorum superficialis or flexor carpi ulnaris or the carpi radialis to the extensor digitorum communis. For the thumb extension, you can transfer the palmaris longus or the flexor digitorum superficialis to extensor pollicis longus. In low velocity gunshot wound to the humerus you will use coaptation splint , even in the presence of radial nerve palsy.
SURGICAL APPROACHES AND IATROGENIC RADIAL NERVE PALSY
There is 20% incidence of nerve palsy from the lateral approach, 10% from the posterior approach and 5% from the anterolateral approach . During posterior approach to repair a fracture of the distal third of the humerus you can identify the radial nerve 4cm proximal to the triceps aponeurosis . In anterolateral approach radial nerve lies between brachialis and brachioradialis muscle. If the nerve palsy occur from surgery then you are going to watch for radial nerve recovery. If it occurs from manipulation and reduction then it becomes controversial. Some people will explore the nerve and some people will wait and observe the nerve recovery.
Leave a Reply