Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
ELBOW PAIN CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- Elbow pain has several common causes
- It is important to make the correct cause of elbow pain so that appropriate treatment can be give to the patient
- The site and location of different causes of elbow pain appears to be close to each other
- It may be difficult to determine the source of the pain and this makes diagnosis of elbow pain difficult or confusing
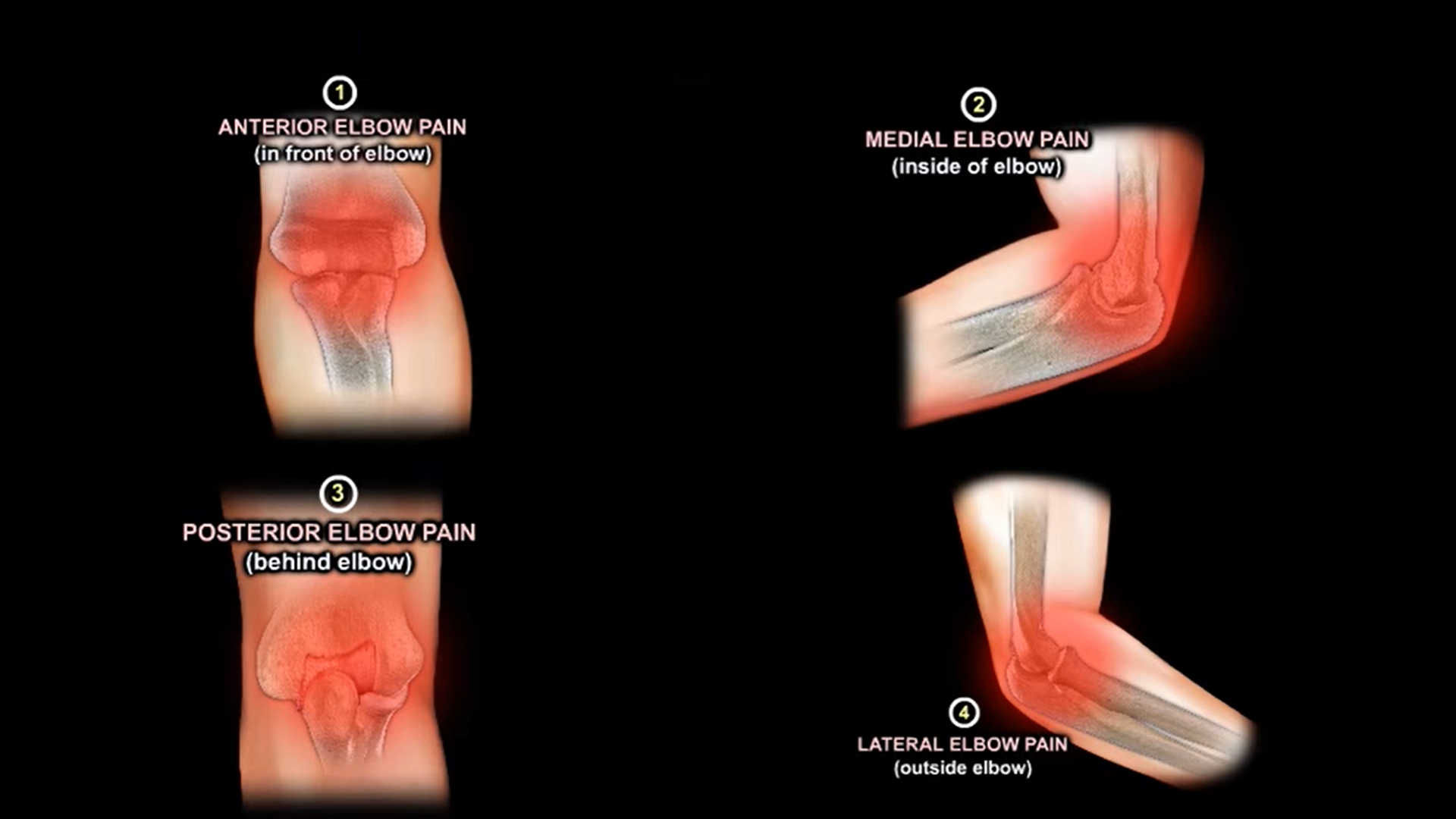
Common causes of elbow pain
1. Anterior elbow pain (In front of the elbow)
2. Medial elbow pain (Inside of the elbow)
3. Posterior elbow pain (Behind the elbow)
4. Lateral elbow pain (Outside of the elbow)
Anterior elbow pain
a) Rupture of the distal biceps tendon. The biceps tendon inserts into the radial tuberosity. It helps in flexion of the elbow and supination of forearm. When the distal biceps tendon ruptures, the patient will have pain, bruising and swelling located in front of the elbow. The injury is found in people who perform manual labor and in body builders. When rupture occurs, the tendon and muscle may retract proximally, causing Reverse Popeye sign. The rupture has an effect on 40% of supination of the forearm and the tendon needs to be reattached to the tuberosity of the radius.
b) Elbow arthritis
Elbow injuries can lead to loss of cartilage and joint degeneration due to extra wear and tear on the surfaces of the joint. This condition is called osteoarthritis, degenerative arthritis or post-traumatic arthritis. Patient has global pain, stiffness and loss of motion.
TREATMENT:
• Anti-inflammatory medication
• Physical therapy
• Injections
• Surgery
Medial elbow pain
The common flexor tendon and the flexor muscles of the forearm are responsible for the flexion of the wrist
a) Golfer’s elbow
Golfer’s elbow is medial epicondylitis. It involves the flexor muscle group. It is an inflammation, soreness or pain on the inside (medial) aspect of the elbow. This pain is due to repetitive overuse or overload activities and it is aggravated by movement of the wrist.
TREATMENT:
• Ice
• Decreased activity
• Physical therapy
• Eccentric exercises
• Injections
• Surgery- last resort
b) Cubital tunnel syndrome
It occurs due to compression of the ulnar nerve at the medial side of the elbow resulting in pain, swelling, weakness of the hand and decreased sensation in the medial 1½ fingers. The problem occurs due to compression where the ulnar nerve passes around the elbow through the cubital tunnel.
TREATMENT:
Conservative treatment first and surgery if conservative treatment fails.
c) Medial collateral ligament injury (MCL injury)
- The injury typically occurs in throwing sports such as baseball as seen in pitching (Tommy John injury). It can then lead to chronic pain as well as valgus instability and the condition can be potentially disabling.
TREATMENT:
- Stop throwing
- Physical therapy
- Evaluation with X-Rays or MRI
- Injury may need reconstruction, which is successful, but it will take a long time to restore the function of the elbow.
Posterior elbow pain
a) Posterior impingement syndrome
Valgus extension overload. Extension overload and valgus stress can result in injury of the posterior part of the elbow. Athletes present with posterior elbow pain that is worsened when the elbow is extended with loss of velocity and control. The athlete may experience catching, locking, clicking and stiffness. With repeated forced extension of the elbow, the tip of the olecranon is jammed into the fossa at the back of the elbow causing inflammation, cartilage injury, loose fragments and bony spurs.
TREATMENT: Usually conservative and rarely surgery.
b) Olecranon bursitis
- It is the inflammation of a small sac of fluid located at the tip of the elbow. This bursa allows the elbow to bend and straighten freely underneath the skin but can become irritated with repetitive movement.
TREATMENT: Usually conservative and rarely surgery
Lateral elbow pain
a) Tennis elbow (Lateral epicondylitis)
It occurs due to injury or pathology of the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis muscle. It is an inflammation, soreness or pain on the outer (lateral) side of the elbow. The injury is usually seen in patients who perform manual labor or sports that require twisting or extension of the wrist against resistance. The extensor muscles of the forearm are responsible for the extension of the wrist. There will be pain with resisted wrist extension, degeneration, irritation and tears of the extensor tendon.
Differential diagnosis: Radial tunnel syndrome. The pain is usually distal to the lateral epicondyle radiates down to the forearm. If the symptoms of tennis elbow are not going away with treatment, then rule out the possibility of radial tunnel syndrome.
TREATMENT:
• Ice
• Elbow pads
• Decreased and modified activity
• Physical therapy- Eccentric exercises
• Injection- Steroid injection. May use PRP
• Surgery- last resort
b) Posterolateral rotator instability of the elbow
Can occur due to excessive debridement and release of the tendon of the ECRB and this can lead to injury of the lateral collateral ligament.
Leave a Reply