Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Sciatic nerve course and branches to the leg and foot
• The sciatic nerve ends just above the popliteal fossa , by dividing it in to :
1. Common peroneal nerve
2. Tibial nerve
• Tibial nerve supplies the posterior muscles of the leg:
1. Medial and lateral head of the gastrocnemius
2. Soleus
3. Tibialis posterior
4. Flexor digitorum longus
5. Flexor hallucis longus
• The common peroneal nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve that travels posterior to the tendon of biceps femoris and it passes across the neck of fibula.
It pierces the peroneus longus and then divides in to
1. Superficial peroneal nerve
2. Deep peroneal nerve
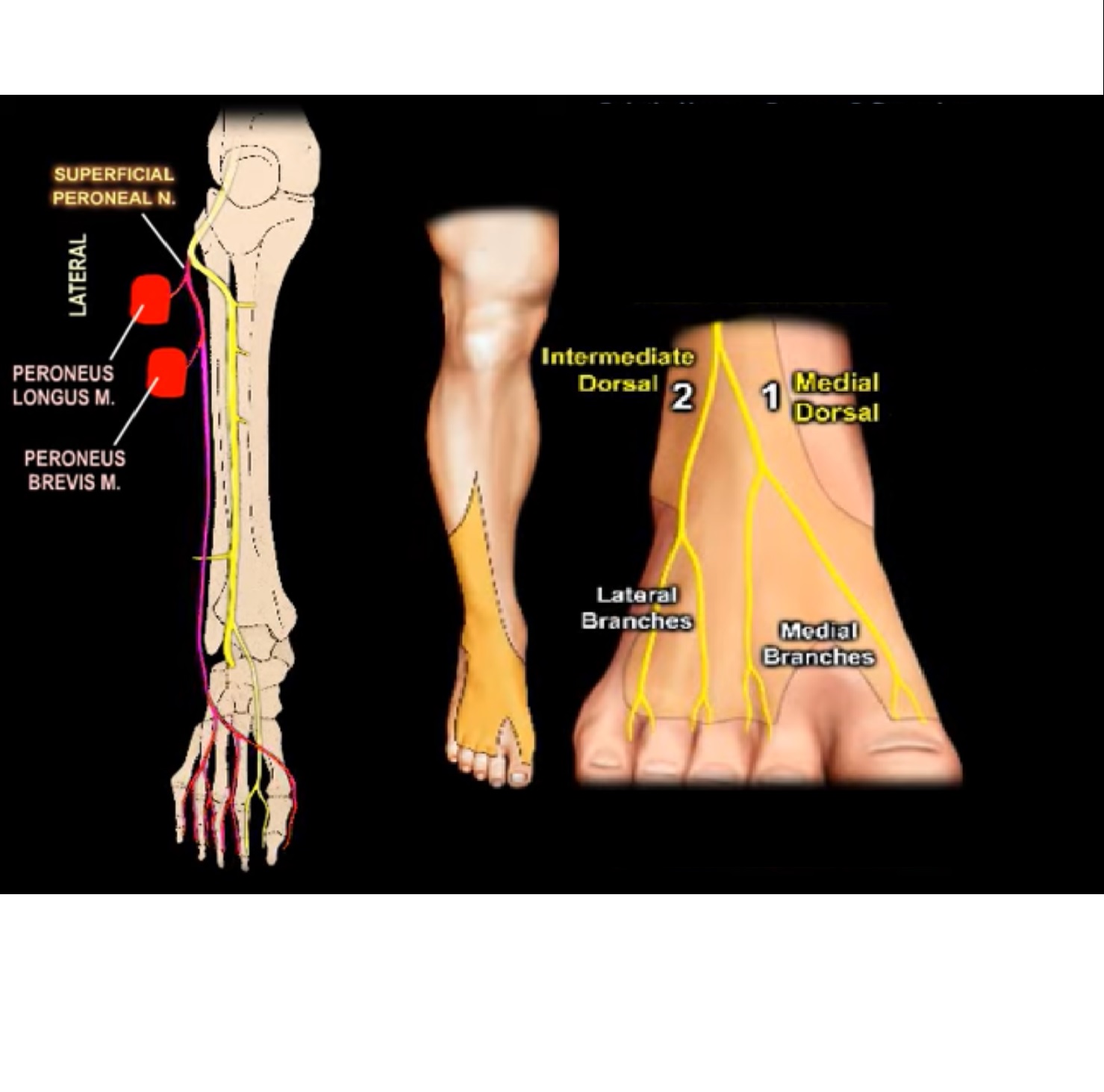
Superficial peroneal nerve:
• Supplies muscles of lateral aspect of leg– peroneus longus and peroneus brevis.
• Superficial peroneal nerve is called superficial or sub cutaneous because some part of the nerve go through the muscles and some parts are cutaneous
• In the proximal part of the leg the superficial peroneal nerve goes through the substance of the peroneus longus muscle .
• In the middle third of the leg the superficial peroneal nerve is located between the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscle.
• It is seen in the groove between the peroneus brevis and extensor digitorum longus muscle.
• In the distal 3rd of the leg the superficial peroneal nerve then pierces the fascia to become superficial .
• In the ankle the superficial peroneal nerve divides in to intermediate , dorsal cutaneous and medial dorsal cutaneous branches.
• Superficial peroneal nerve has a variable course and it becomes superficial to the peroneus longus muscle in the distal third of the leg.
• Superficial peroneal nerve divides in to sensory branches that supply the skin of the dorsum of foot.
• Function: eversion of foot
• Injured during fasciotomy of the lateral compartment of the leg
Deep peroneal nerve :
• Supplies the muscles of anterior compartment of the leg—tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, peroneus tertius ,extensor digitorum brevis
• It gives a sensory branch to first web space, b/w 1st and 2nd toes – helps in diagnosing compartment syndrome
• Function: dorsiflexion of ankle and the toes
• Causes foot drop
Tibial nerve
• Passes in to foot , running posterior to the medial malleolus and beneath the flexor retinaculum
• It divides in to:
1. Medial and lateral plantar branches
2. Medial calcaneal branch
• Tibial nerve gives innervation to all muscles of foot except the extensor digitorum brevis
• Medial plantar nerve gives branches to
1. Abductor hallucis
2. Flexor digitorum brevis
3. Flexor hallucis brevis
4. First lumbricals
5. Digital nerves to medial 3 ½ toes
• Therefore medial plantar nerve innervation is similar to innervation of median nerve in the hand
• Lateral plantar nerves gives digital nerves to
1. Lateral 1 ½ toes
2. Abductor digiti minimi
3. Quadratus plantae
4. Adductor hallucis
• Similar to ulnar nerve in the hand, it gives branches to all interossei and from the 2nd to the 4th lumbricals
• It is the nerve which gives innervation to most intrinsic muscles of foot
• Baxters nerve: 1st branch of lateral plantar nerve: important in d/d of plantar fascitis
Leave a Reply