Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Deltoid muscle
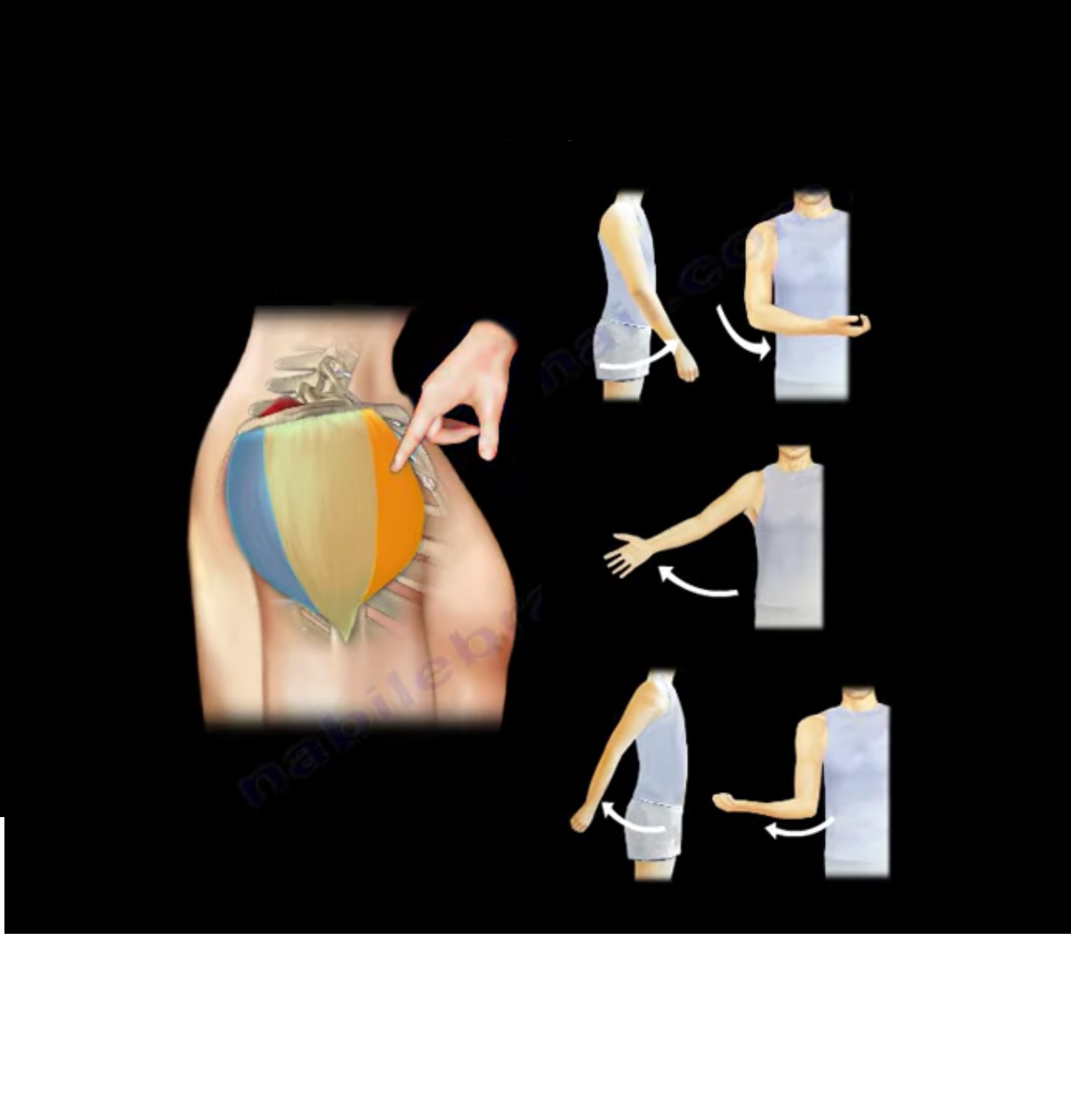
Anatomy
3 parts(on the basis of its three origins)
1. Anterior part(lateral 1/3 rd of clavicle)
2. Lateral/acromial part(acromion of scapula)
3. Posterior part/spinal part(spine of scapula)
Function of various parts
• Anterior-flexes and medially rotates the arm
• Lateral-abduction of arm upto horizontal level
• Posterior-extends and laterally rotates the arm
Insertion• Deltoid tuberosity in humerus(fibres join together to form a short tendon)
Facts
• Anterior to posteriorly bulk of the deltoid muscle encircles the shoulder joint
• Shoulder and deltoid muscle gets its round appearance due to deltoid passing over upper part of humerus.
Nerve supply
• Axillary nerve(motor supply to deltoid, sensory supply to shoulder area)
Axillary nerve
• Origin: a terminal branch of posterior cord of brachial plexus
• Course: runs transversely from posterior to anterior about 7 cm distal to acromion
• Injury of axillary nerve:
Cause of injury: during fracture or dislocation of shoulder joint
clinical findings
- Weakness of abduction
- Atrophy of deltoid muscle
- Flattening of shoulder
- Loss of sensation over shoulder area
Arterial supply:
• Anteriorly: thoracoacromial artery(branch of axillary artery)
• Posteriorly: posterior circumflex humeral artery
Quadrangular space:
• Bound by humerus, long head of triceps, teres major, teres minor
• Contents: posterior circumflex humeral artery and axillary artery
Rupture of deltoid muscle
Causes of damage of deltoid:
• Sports or heavy manual labour
• Surgery that require release of deltoid muscle from its origin
• Surgery of os acromiale
• Total acromionectomy
- Arthroscopic procedures are better than open shoulder procedure
- Rupture should be repaired or reconstructed
Applied anatomy
1. Danger of lateral approach
• Axillary nerve runs transversely from 7 cm distal to acromion
• Incision should not be more than 5 cm distal to the acromion to protect axillary nerve damage
• In fixation of proximal humerus where incision needed to be made distally, additional anterolateral incision over humeral shaft should be made to avoid axillary nerve injury
2.deltoid intramuscular injection
• Injection site:3-5 cm distal to acromion, in middle of lateral part of deltoid
• Should not exceed 5 cm distal to acromion (danger zone of axillary nerve injury)
• High injection avoided as it may enter capsule/shoulder joint
• Low injection avoided as it causes neurovascular injuries
Leave a Reply