Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
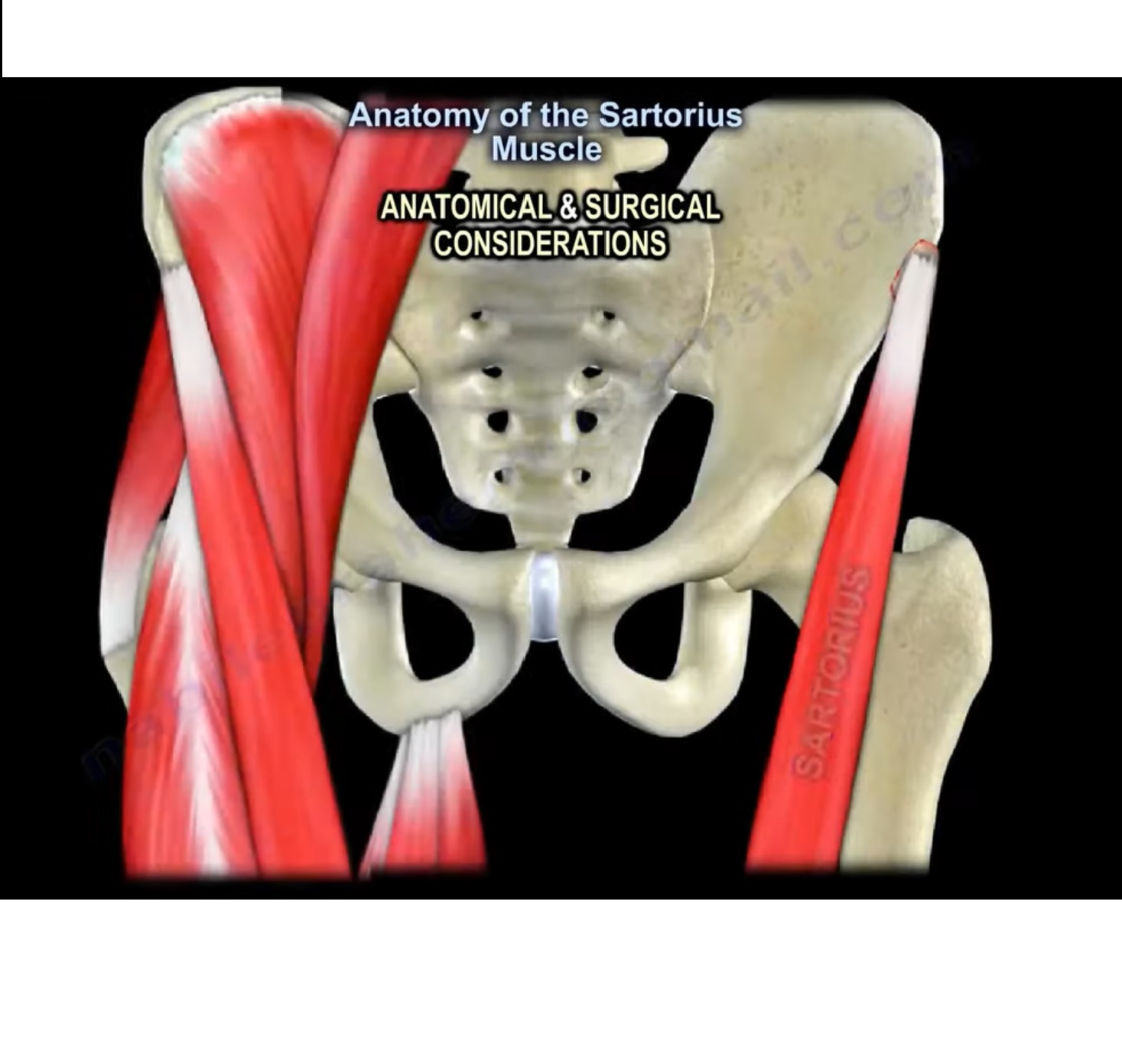
Anatomy of Sartorius
Introduction:
It is a superficial muscle and the longest muscle of the body with parallel fibres located over the anterior aspect of thigh.
Attachments:
Origin:
It takes its origin at the anterior superior iliac spine of pelvic bone.
Insertion:
It is inserted to the anteromedial upper surface of tibia, where 2 other muscle tendons (gracilis and semitendinous) also gets inserted to form pes anserine.
Course:
It crosses the upper third of thigh obliquely, downwards medially and the descend vertically towards its insertion.
Nerve supply:
The sartorius is innervated by femoral nerve.
Function:
The main actions of sartorius muscle are flexion, abduction and lateral rotation of hip and flexion of knee. Due to this action, it is also called as the “tailor’s muscle”, because it helps to position the leg in the way the tailors once did.
Anatomical significance:
- The upper third of the sartorius forms the lateral border of femoral triangle.
- Middle third forms the roof of adductor canal.
Clinical significance:
- Anterior approach to hip (smith peterson approach): The neurovascular bundle passes medial to sartorius, hence it is better to approach the hip anteriorly from lateral aspect of sartorius.
Bony avulsion of sartorius tendon:
- It occurs due to a strong sudden pull of sartorius with hip in extended position and knee in flexion. It is commonly seen in sprinters and running athletes.
- Also when taking up iliac crest graft graft, it is always better to take it atleast 3cm away from ASIS in order to prevent avulsion.
FEMORAL TRIANGLE:
- It is a superficial triangular space located in the anterior aspect of thigh just inferior to inguinal ligament.
Boundaries:
- Lateral border is formed by the medial border of sartorius.
- Medial border is formed by the medial border of adductor longus.
- Base is formed by inguinal ligament.
Contents:
From lateral to medial the contents of this triangle are femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein and deep inguinal ligaments.
ADDUCTOR CANAL(SUBSARTORIAL CANAL)
- it is an aponeurotic tunnel in the middle third of thigh extending from apex of femoral triangle to the opening of adductor magnus (adductor hiatus).
- The contents of this canal include femoral artery, femoral vein and saphenous nerve ( branch of femoral nerve).
PES ANSERINE BURSA:
- Pes anserine bursa is a small fluid filled sac situated between tibia and the three tendons of sartorius, gracilis and semitendinous.
- Innervation: the sartorius is innervated by femoral nerve, gracilis by obturator nerve and semitendinous by tibial branch of sciatic nerve.
Pes anserine bursitis ( breast stroke knee):
- It is an inflammatory condition of medial aspect of knee at pes anserine bursa.the patient mainly presents with pain over medial aspect of knee, tenderness below the joint line on medial part of proximal tibia, and a localised swelling.
- It usually follows a trauma or can be iatrogenically induced by total knee replacement.
Leave a Reply