Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
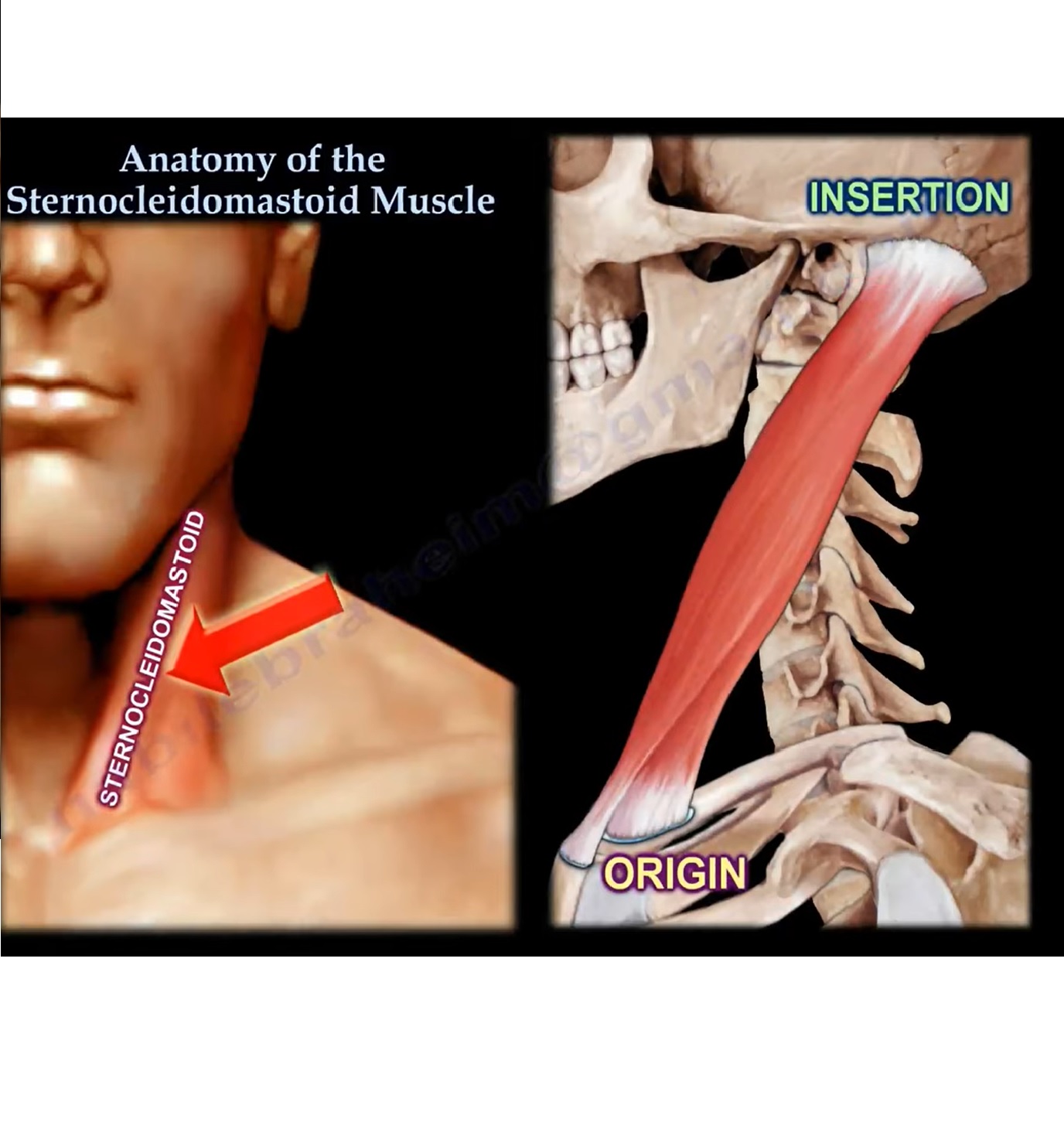
ANATOMY OF STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID
INTRODUCTION:
Sternocleidomastoid, shortly called as STERNOMASTOID, is one of the largest and most superficial
cervical muscle situated in the superficial layer on the side of neck.
ORIGIN:
The muscle has two origins.
- STERNAL HEAD
- CLAVICULAR HEAD
The sternal head is located at MANUBRIUM STERNI whereas the clavicular head is located over
the medial portion of clavicle
INSERTION:
- The muscle is inserted over the lateral surface of mastoid process of the temporal bone and
lateral half of the superior nuchal line of occipital bone.
NERVE SUPPLY:
- The muscle is given its motor innervation by SPINAL ACCESSORY NERVE (XI cranial nerve).
FUNCTION:
- The muscle mainly helps in tilting the head to same side and rotating the head to opposite side.
- Muscles of both sides act simultaneously to tilt the head downwards.
ANATOMICAL RELEVANCE:
- Sternocleidomastoid divides the region of the neck into an ANTERIOR TRIANGLE and a POSTERIOR
TRIANGLE.
CLINICAL RELEVANCE:
- Contracture of STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID: It is known as CONGENITAL MUSCULAR TORTICOLLIS. The infant holds his head tilted to one side and has difficulty in turning the head which happens due to tight and shortened muscle.
DISPLACEMENT OF CLAVICLE FRACTURE:
- During fracture of clavicle, the proximal fragment is pulled upwards by the action of SCM whereas
the distal fragment sags down due to gravity and weight of the arm.
Leave a Reply