Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
LOW BACK PAIN
- When the patient comes to you for evaluation of low back pain,the first question that you would ask is if the patient has any bladder or bowel problems.
- You want to separate low back pain or acute low back pain from cauda equina
- Cauda equina syndrome is an orthopaedic emergency. It needs to be diagnosed early and treated by surgery early.
1. Make sure that you do not miss cauda equina syndrome.
2. Ask the patient about any bladder or bowel changes.
3. If there is any concern, then you need to get a MRI
Acute low back pain or low back pain with sciatica(pain radiating to the lower leg and to the foot
Both conditions are initially treated conservatively for at least 6 weeks by:
- Physical therapy.
- Anti-inflammatory medication.
- Limited activity(as guided by the pain).
- Treat the condition conservatively even if there is a big disc herniation on the MRI-wait atleast 6 weeks.
- 90% of patients will have symptoms resolve in 1 month.
- Smoking, depression, and vibrations will increase the incidence of low back pain.
Intradiscal pressure changes with position-the lowest pressure is in supine position and the highest pressure in sitting leaning forward and holding weight.
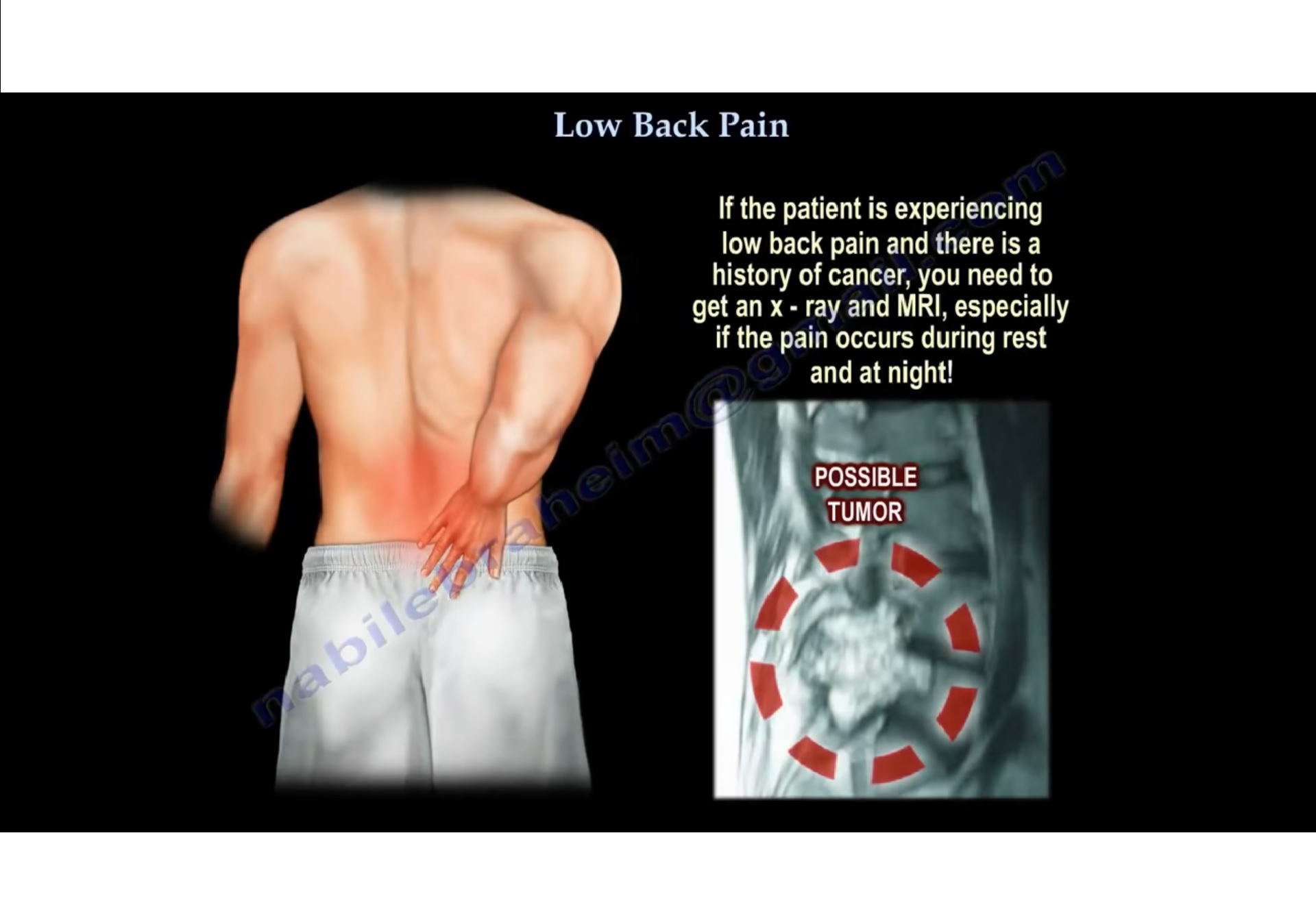
- If the patient is experiencing low back pain & there is a h/o cancer, you need to get an x-ray and MRI especially if the pain occurs during rest and at night.
- In case of a renal tumor, you will probably need to do arteriography and embolization of the spinal lesion.
- The spine is a common location for metastatic tumors. Metastases occur in the vertebral body and goes to the pedicle.
- Loss of about 30%-40% of the bone mass should occur before we can detect the lesion on x-ray.
- Loss of the pedicle bone will give us a “winking owl sign”
Infection:
- If infection occur within the intervertebral disc space, The ESR and CRP levels will be elevated.
- Only 50% of the cases will have fever and less than 50% will have an elevated WBC.
- Get a blood culture(positive in about 24% cases)
- Get an MRI and give antibiotics as guided by the biopsy, culture and sensitivity.
- If the patient has an epidural abscess, you will do surgery, especially if there is deterioration of the neurological function.
- If there is infection post-surgery, you can diagnosis it with a high CRP.
Osteoporotic fracture
- Osteoporotic bone is at risk of fracture at wrist, spine and hip
- If you have an osteoporotic spine, you need to treat it before it leads to a hip fracture later on.
- One fracture of the spine will leads to more spine fractures.
- After 1 year of treatment with medication, the incidence of vertebral fracture is decreased by 60% and after 2 years by 40 %.
When you are dealing with a patient with low back pain:
- Treat the patient conservatively.
No need for x-rays in the first 4-6 weeks unless there are some such as:
- Patient is older.
- Patient has a metastatic tumor/ history of cancer.
- Infection is suspected.
- Patient has trauma.
- Osteoporotic fracture due to steroid use.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis starts at the SI joint.
- X-ray shows ” bamboo spine”. you may find marginal syndesmophytes with diffuse ossification of the disc space without large osteophyte formation.
- HLA-B27 positive.
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis(DISH)
- Get a HbA1c test.
- Syndesmophytes are non- marginal and have larger osteophytes.
- They have flowing ossification along the anterolateral aspect of at least four continuous vertebra.
- Get an MRI of the spine at a certain point, however you need to start first by getting x-rays.
MRI may be a problem!
- There are abnormal MRIs in asymptomatic patients(there are false positive)
- 35% in patients above 40 years of age.
- 90% positive MRIs in asymptomatic patient over 60 years of age.
Leave a Reply