Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
ANATOMY OF PERONEAL MUSCLES IN LOWER LEG
INTRODUCTION :
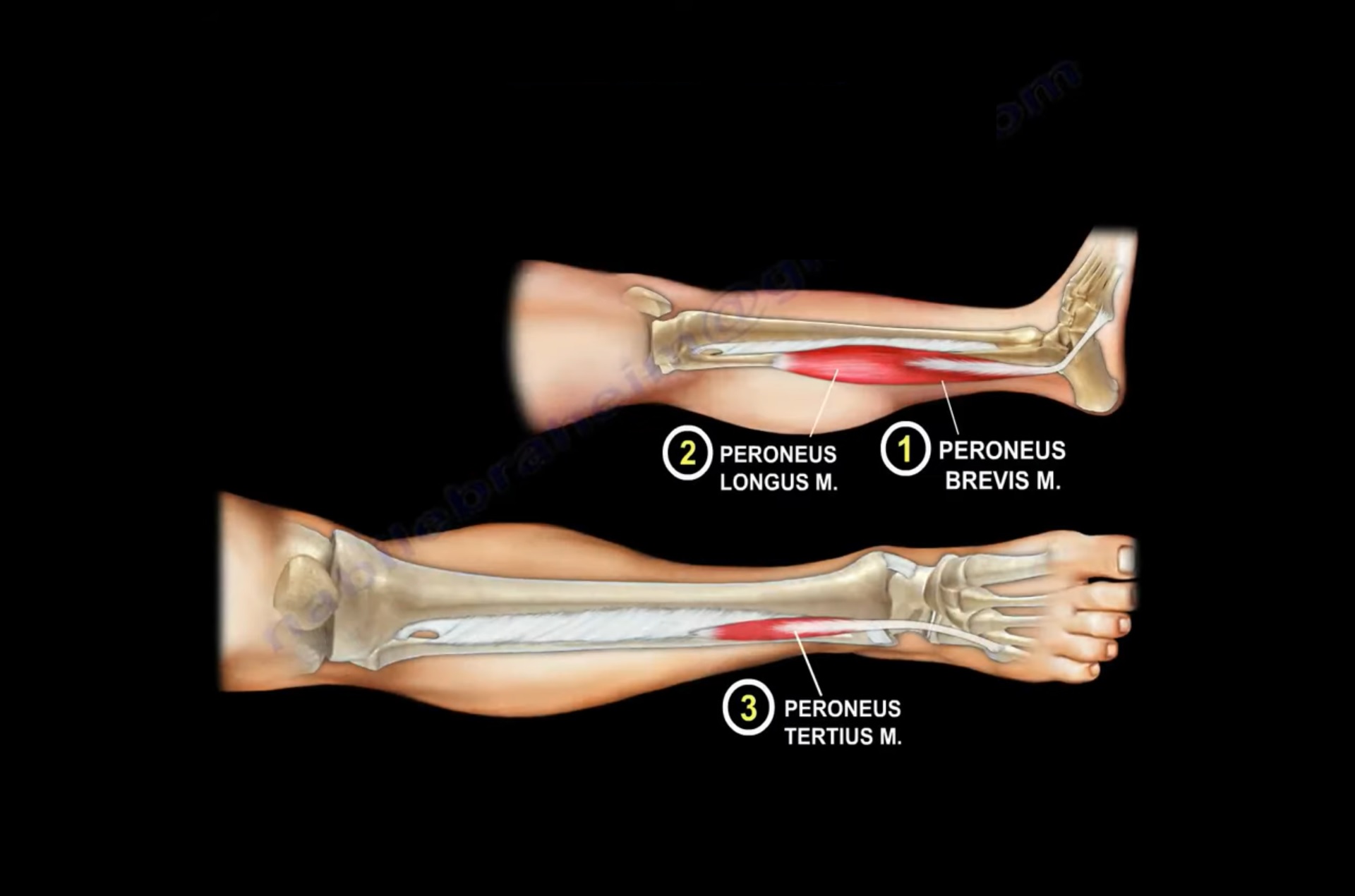
Peroneal muscles consist group of 3 muscles:
- Peroneus longus
- Peroneus Brevis
- Peroneus Tertius
- Peroneus longus and P.brevis lies within the lateral compartment where as P. Tertius is located within the anterior compartment of the leg.
ATTACHMENTS:
Peroneus Longus :
Origin : It originates from the upper 2/3rd of lateral surface of fibula. It is the longest and superficial muscles of lateral compartment.
Insertion : It inserts to 2 bones . base of 1st metatarsal and adjoining part of medial cuneiform bone.
Peroneus Brevis :
Origin : It originates from the lower 2/3rd of lateral surface of fibula. It can be used as a flap to reconstruct small defects of distal 3rd of lower leg.
Insertion : It inserts to tuberosity of base of 5th metatarsal bone.
Peroneus Tertius :
Origin: It originates from the lower1/3rd of anterior portion of medial surface of fibula.
Insertion: It inserts to dorsal surface of base of 5th metatarsal bone.
The peroneal muscles are situated on the outer side of lower leg and their tendons are attached to the foot.
Peroneal Retinaculae: There are 2 peroneal retinaculae which holds the two peroneal tendons.
- Superior peroneal retinaculae
- Inferior peroneal retinaculae
- Rupture of Superior peroneal retinaculae may cause tendon subluxation. It can be acute, chronic, recurrent.
- Acute rupture causes subluxation of peroneal tendon and may cause disability of ankle.
- Persistent swelling along the the posterolateral edge of fibula is the most reliable sign . Retromalleolar pain on active eversion is specific
- “Fleck sign” indicates the peroneus tendon subluxation, sometime call this as avulsion fracture of fibula , the rim fracture.
- Tear of superior retinaculae may be misdiagnosed because of associated pain, swelling and ecchymosis that may hinder early diagnosis.
INNERVATION :
- P. Longus and P. Brevis is supplied by superficial peroneal nerve.
- P.Tertius is supplied by deep peroneal nerve.
FUNCTION :
- Peroneus Longus : It helps in plantar flex of the foot , eversion as well as maintain the transverse arch of the foot.
- Peroneus Brevis : It helps in the eversion of the foot.
- Peroneus Tertius : it helps in eversion of the foot and dorsiflex the foot at the ankle joint.
Leave a Reply