Courtesy: Sally Hobson, Hull Royal Infirmary, Hull, UK
Perthes Disease
Definition:
- Idiopathic osteonecrosis of capital femoral epiphysis in a growing child.
Epidemiology: –
- Males 4x females.
- 80% 4-9 (2-12 reported).
- Social class 4-5.
- Bilateral 10%:
- Usually asymmetric.
Presentation – history
- Limp.
- +/- hip/knee pain.
- Usually insidious/chronic onset.
Presentation – examination
- Reduced ROM – ABDUCTION.
- Ataxic/trendelenberg gait.
- Wasting thigh/buttock.
- FFD, limited rotation.
- LLD:
o Adduction contracture.
o True shortening due to collapse CFE.
Differential Diagnosis
- Acute presentation versus chronic post AVN hip xray.
- Unilateral versus bilateral.
Infection.
Inflammatory.
Skeletal dysplasia (MED).
Haematological:
o Sickle cell/thalassaemia.
o Haemophilia.
o Leukaemia.
Metabolic.
Trauma.
Iatrogenic (DDH
Investigations
- FBC/Inflammatory markers – exclude dd.
- X-ray diagnosis – only miss if very early presentation.
- Bone scan, MRI not usually required.
- Arthrogram / EUA can be useful.
Classification
- Catterall:
% of head involvement 25/50/75/100.
Herrings lateral pillar classification:
o Comparison to contralateral, normal side.
o Based on the worst x-ray in the series.
A – lateral pillar preserved.
B ->50% maintained.
C – > 50 % involved
Aetiology
- Poorly understood.
- ?infection.
- ?trauma.
- ?transient synovitis.
- ?clotting abnormality
- ?vascular changes primary or secondary to cartilage disorder.
Pathology – stages
- Early/infarction.
- Intermediate/fragmentation.
- Healing.
- Remodelling.
- Whole disease process over several years.
Pathology – sclerotic
Infarction:
o Early – Hypertrophy of cartilage and reduced epiphyseal height.
o Later – Sclerosis, subchondral fracture (crescent sign).
Pathology – fragmentation
- Necrotic bone replaced by fibrocartilage.
- Revascularisation by creeping substitution.
- Areas of unossified cartilage stream across physis into metaphysis (cysts) – can cause growth arrest.
Pathology – healing
- Endochondral ossification – fibrocartilage reossifies.
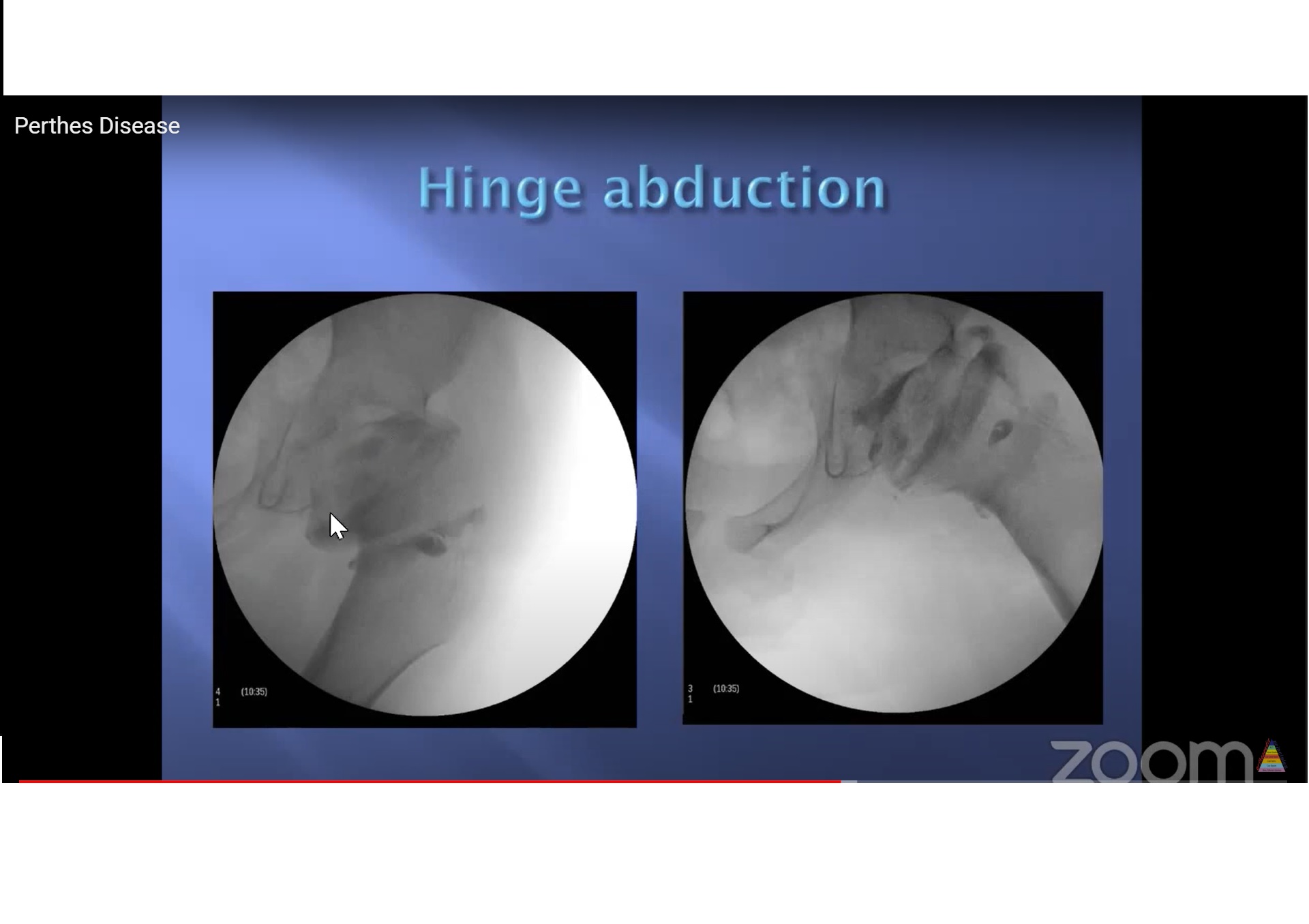
- Last portion to form is anterosuperior epiphysis – round head becomes oval – can produce hinge abduction
Pathology – remodelling
Treatment – non-operative
- Bed rest.
- (Traction)
- Activity modification/crutches.
- Analgesia.
- Physio to maintain ROM.
? (Abduction brace). - Herring says NONE of these affect outcome.
- Follow up patients 3-6 monthly depending on stage in disease and if considering surgery.
Treatment – operative
- Containment (in early/fragmentation phase):
- EUA arthrogram to assess.
Options:
o Proximal femoral osteotomy.
o Salter osteotomy.
o Shelf osteotomy.
?Hip distraction.
Outcomes
Herring says:
o A all do well regardless of treatment and age.
o C all do badly regardless of treatment and age.
o B – outcome improved by surgery IF patient over 8yrs.
- High rates of future OA/need for THR.
- Worse with higher Stulberg grade.
Treatment – salvage
- Valgus extension osteotomy.
- Chiari.
- Cheilectomy.
- Arthroplasty
Conclusion
- Aetiology unclear.
- Typical presentation but remember differential diagnoses.
- Predictable pathology.
- Treatment and assessment of outcome controversial:
o EUA/arthrogram to plan.
o Maintain ROM.
o Containment.
o Salvage surgery for painful hinge abduction.
Leave a Reply