Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
COMMON PAEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES
It can include;
1)supracondylar fractures of humerus
2) paediatric elbow fractures that involve the ossification centres.
Here we are dealing with:
PAEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES THAT INVOLVE THE OSSIFICATION CENTRES.
TRANSEPIPHYSEAL SEPARATION OF THE DISTAL HUMERUS
- Suspect child abuse in these injuries.
- It is usually confused with elbow dislocation, however in elbow dislocation the elbow moves posteriorly and laterally.
- In Transepiphyseal separation Olecranon moves posteriorly and medially.
- The child is too young to have an elbow dislocation.
- One important key here is that the radiocapitellar line remains the same(it is not interrupted ).
- If the radiocapitellar shows that the capitellum and the radial head are aligned , then it is not an elbow dislocation. It is a transepiphyseal separation.
- The diagnosis is usually difficult and can be missed.it should be highly suspected with elbow injuries before the age of one year.
- Understanding when the ossification centres appear around the elbow is important.
(Ages when the ossification centres appears around the elbow are as : )
- Capitellum 1 year
- Radial head 3 year
- Internal epicondyle (medial)5 year
- Trochlea 7 year
- Olecranon 9 year
- External epicondyle(lateral) 11 year
2.LATERAL CONDYLAR FRACTURE
- Lateral epicondylar fractures are usually Salter-Harris Type IV Fractures.
- If the fracture appears nondisplaced ,then you need to get an internal rotation view of the elbow that will show you the amount of the displacement of the fracture.
- If you decide to treat the nondisplaced fracture conservatively, then you need to have close follow up with repeat x-rays at short intervals to make sure that the fracture does not displace. It is a joint injury!
- The majority of the fractures will appear displaced and the surgery should be done with a lateral approach and not a posterior approach.
- The posterior approach will compromise the blood supply of the capitellum and can cause avascular necrosis .
Complications of the lateral condylar fracture
1. NON UNION
Cubitus valgus :it happens because the medial part of the elbow will grow more than the lateral part that is injured and the elbow will be in valgus.
2. ULNAR NERVE SYMPTOMS
It takes years to develop ulnar nerve symptoms because the ulnar nerve gets stretched by the cubitus valgus.
TREATMENT
- If the non union happens and the patient has good motion of the elbow but complains of pain , then you will do bone graft and fixation.
- If there are associated ulnar nerve symptoms , then you need to release or transpose the ulnar nerve.
Lateral condylar fracture of humerus is a surgical case ! no question about it.
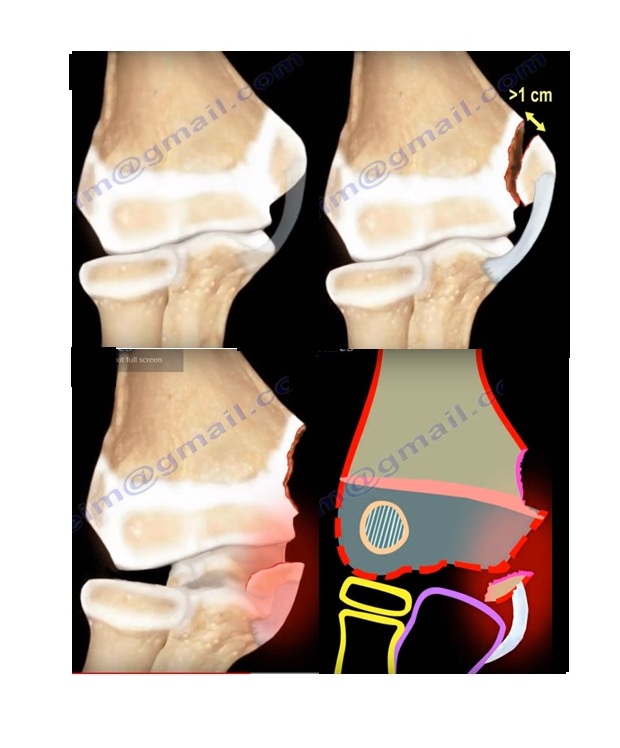
3.MEDIAL EPICONDYLE
- The medial epicondyle growth plate is the last one to fuse.
- Fracture of the medial epicondyle is treated conservatively.
- If there is displacement more than 1 cm ,then the surgeon may decide to do surgery.
- The amount of displacement that requires surgery is controversial.
- The medial epicondyle fracture is commonly associated with dislocation of the elbow.
- Look for the medial epicondyle on the post reduction x rays.
- If the medial epicondyle fragment becomes trapped in the elbow joint then it needs to be removed and fixed.
4.RADIAL HEAD AND NECK FRACTURES.
- Conservative management should be done if there is less than 30 degrees of angulation or 30 degrees of displacement.
TREATMENT
- Closed reduction is done if displacement is more than 30 degrees.
- Percutaneous pin may be used for reduction as joystick.
- Open reduction is done if there is more than 45 degrees of residual angulations after failure of closed reduction or percutaneous joystick method.
Complications:
SYNOSTOSIS
- Fusion of the radius to the ulna.
- Reflected periosteum is a possible cause of synostosis
OSTEONECROSIS
- Due to interruption of the blood supply of the radial head
LOSS OF MOTION OF ELBOW
NON UNION OF THE RADIAL NECK FRACTURE(rare)
- Interposition of the periosteum is a possible cause of nonunion.
Compartment Syndrome
- Radial head fractures may be associated with compartment syndrome.
- Watch for the development of compartment syndrome in a child with radial head fracture.
Leave a Reply