Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
The spine has bony vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
- Inside the spinal canal lies the neural structures. The spinal cord ends at the level of T12- L1. The lower end of the spinal cord is called the Conus medullaris and from the Conus medullaris arises the Cauda equina at level L1, it consists of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets
- Low back pain is caused by various conditions of the lumbar spine including disc herniation.
Disc herniation:
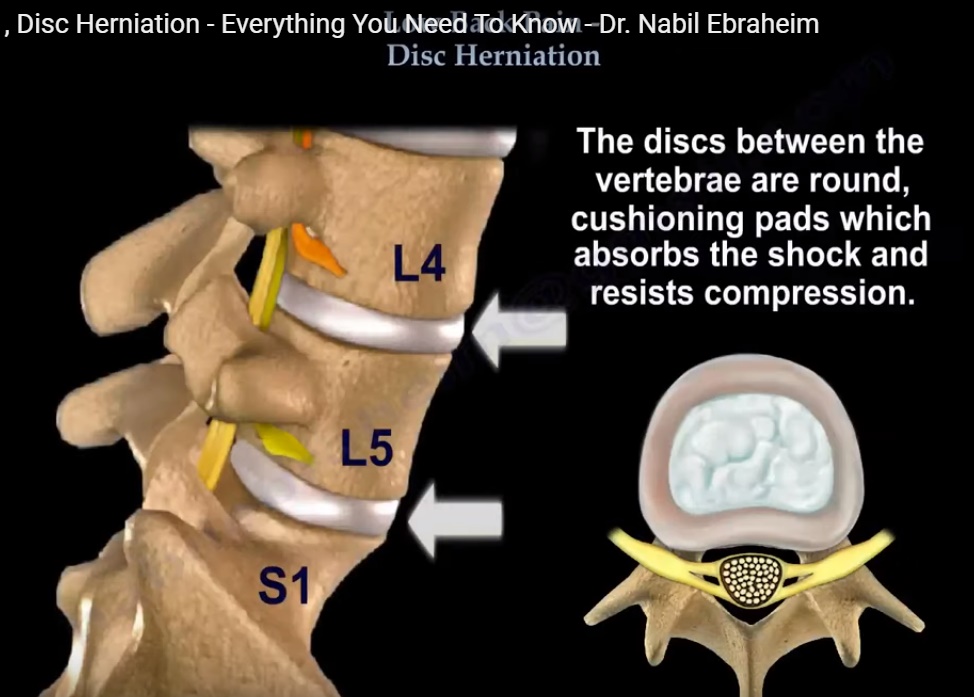
- The lumbar spine has 5 lumbar vertebrae from L1-L5. They are attached to the sacrum at the lower end of the spine which is called the lumbosacral spine (i.e junction between lumbar spine and sacrum) L5-sacrum or tail bone.
- The intervertebral discs between the vertebrae are round and act as a cushioning pad which absorbs the shock and resists compression.
- The intervertebral disc is composed of 2 layers:
1. Nucleus pulposus- it is the inner layer which is a soft gelatinous tissue.
2. Annulus fibrosus- it is the outer layer which is strong and thick. - Behind the disc lies the spinal nerve root and the cauda equina. A lumbar or lumbosacral herniation could affect the nerve roots.
- Majority cases of disc herniation is at the disc levels of L4-L5 and L5-S1.
- The typical herniation of the L4-L5 disc level will affect the L5 nerve root. Likewise herniation of L5-S1 will affect the S1 nerve root.
Types:
1. Protrusion/bulge: It is a bulging disc with intact annular and posterior longitudinal ligament fibres.
2. Disc herniation: It is the disruption of annular fibres with tail of disc material extending into the disc space either partially or totally.
3. Sequestration: Free fragment without tail extending into the disc space. Fragment may be reabsorbed spontaneously.
Locations of disc herniation :
The most common location of disc herniation is
1. Posterolateral: It affects one nerve root (the lower one). For example- L4-L5 posterolateral disc herniation, affects the L5 nerve root.
2. Foramina: Occurs in about 8-10% of cases. It involves the exiting nerve root. For example- L4-L5 foraminal disc herniation will affect the L4 nerve root( nerve root that exits).
3. Central: It is a rare condition involving multiple nerve roots, cauda equina, predominantly causes low back pain more than leg pain. May cause bladder and bowel incontinence. It requires urgent diagnosis and surgical treatment.
Early diagnosis of central disc herniation and cauda equina syndrome is challenging. The initial signs and symptoms are visually subtle. It is important to suspect this condition and ask if the patient is having any bowel and bladder symptoms.
Do per rectal digital examination on the patient, test the perianal sensation and get emergency MRI if you suspect it.
Treatment:
- Usually emergency surgery.
- Timing of the surgery decides the outcome.
- Early surgery has the best prognosis for recovery of the bladder and bowel function.
DISCOGENIC BACK PAIN – INTERNAL DISC DISRUPTION:
- It is an early disc degeneration.
- The patient will have annular tears.
- Pain is worse with flexion/sitting and the pain is slightly better with extension. Forward flexion is limited on examination and the patient does not have radicular symptoms.
Leave a Reply