Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Calcaneal fractures can be intraarticular and extraarticular fractures.
Extra articular fractures
Anterior process fracture
- It results from forced plantar flexion and inversion.
- This fracture is frequently missed and misdiagnosed as an ankle sprain.
- Treatment is usually conservative and surgery is done only in cases
of displaced large fragments.
Tuberosity body fracture results from axial load injury.CT scan may be needed to rule out
intraarticular extension.
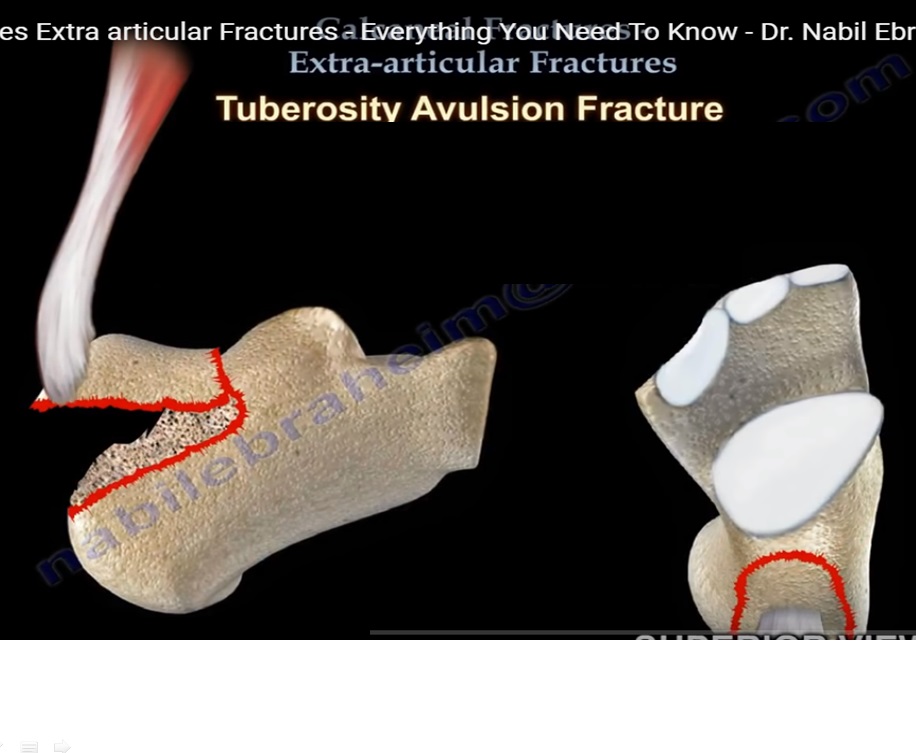
Tuberosity avulsion fracture
- It is the most important extraarticular calcaneal fracture.
- This injury is due to sudden dorsiflexion of gastronemius and soleus muscles,which pulls the Achilles tendon upwards,causing an avulsion fracture.
- This fracture may cause skin compromise at the back of heel.Other predisposinf factors of
avulsion fractures are diabetes and osteoporosis.
Types of avulsion fracture
Type 1 –Sleeve type tuberosity fracture
Type 2-Beak type avulsion fracture
Type 3-infrabursal avulsion fracture
- Most calcaneal fractures are closed injuries that are treated nonoperatively or with surgery when
the fracture is intraarticular and the fracture is displaced. - The timing of surgery is usually after improvement of soft tissue condition.
- Avulsion fractures require urgent care for reduction and fixation of fracture.This will eliminate the risk of skin complications and restore the function of Achilles tendon
Sustentacular fractures
- It results from heel loading accompanied by forced inversion of foot.Surgery is rarely needed.The
flexor hallucis longus tendon is lodged underneath the sustentaculum.
Stress fracture
- Stress fracture of the calcaneum is typically felt deep in the bone and produces a vague complaint of
heel pain. - It is typically seen in atheletes who are overtraining,using improper footwear or those with
mechanical abnormalities. - The pain from stress fracture appears suddenly and remains constant.
- Pain and swelling on both sides of heel can be seen and felt.
- This pain can usually be reproduced by squeezing the heel from both sides(compression/squeeze test).
- This pain can be confused with the pain from plantar fasciitis.
- Plantar fasciitis pain is severe in the morning and when the patient first stands on their feet.Imaging tests may be helpful to confirm diagnosis of a stress fracture.
- This fracture may be difficult to see on xrays until the fracture begins to heal.Early xrays are usually
negative. - Xrays at 4-6 weeks will show the fracture line on posterior aspect of calcaneum as a radiodense vertical line.
- It is best shown on lateral xray of the foot.MRI is usually helpful in the diagnosis,if clinical picture is not clear.
- Treatment is usually conservative.
- Avoid activities such as running and jumping.Use proper footwear to cushion the heel and non weight bearing for 6 weeks utilising a boot or a cast.
Leave a Reply