Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of TOledo, Ohio, USA
Ganglion cyst of the wrist
- Fluid filled cysts that are benign and will not spread.
- It may vary in size from time to time and may grow in size but does not cause harm to the
patient . - When the cysts pressurise an artery, nerve or tendon it causes problem.
- The cysts transilluminates , therefore an MRI is not required.
- The cysts can be dorsal or volar .
- Dorsal type is the most common.
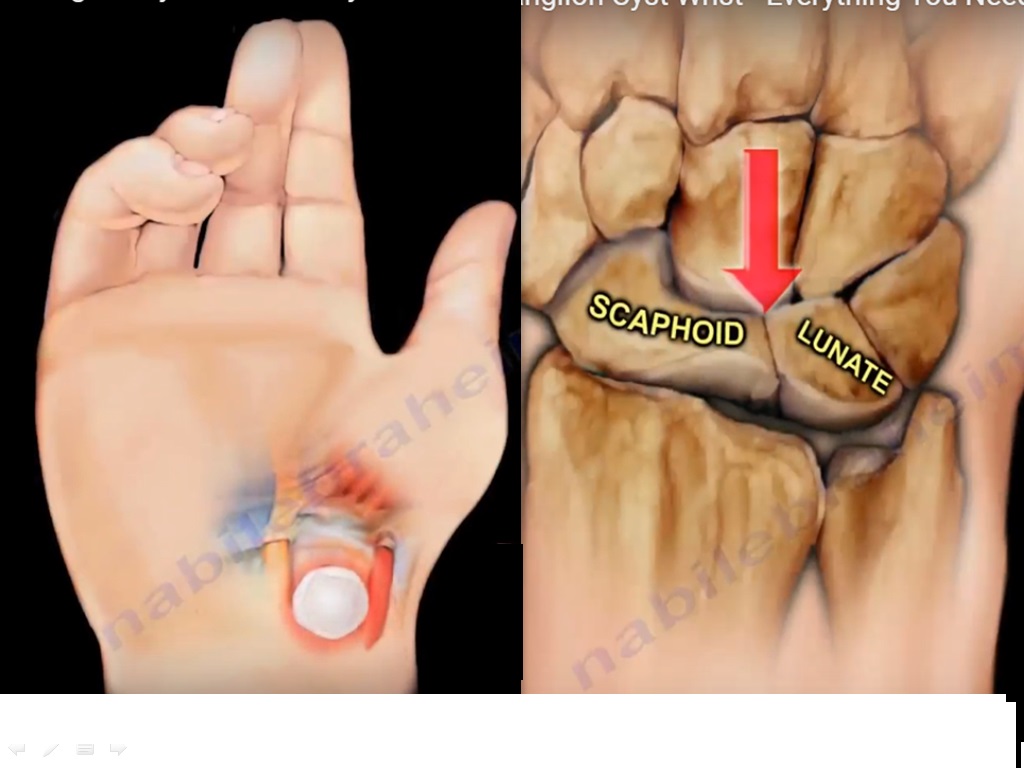
- It arises from the scapholunate articulation.
- The volar ganglion may compress the radial artery and this might compromise the circulation of
hand. - It arises from radiocarpal joint, ie, the wrist.
Clinical findings:
- A mass that is well defined , localized, smooth and not attached to skin.
- Dorsal ganglion cyst is more obvious with flexion of wrist.
- Volar ganglion is more obvious with extension of wrist.
- Ganglion cyst is usually asymptomatic
- Allen’s test is done to see if the cyst is compromising the circulation in case of a volar cyst.
Treatment :
Leave a Reply