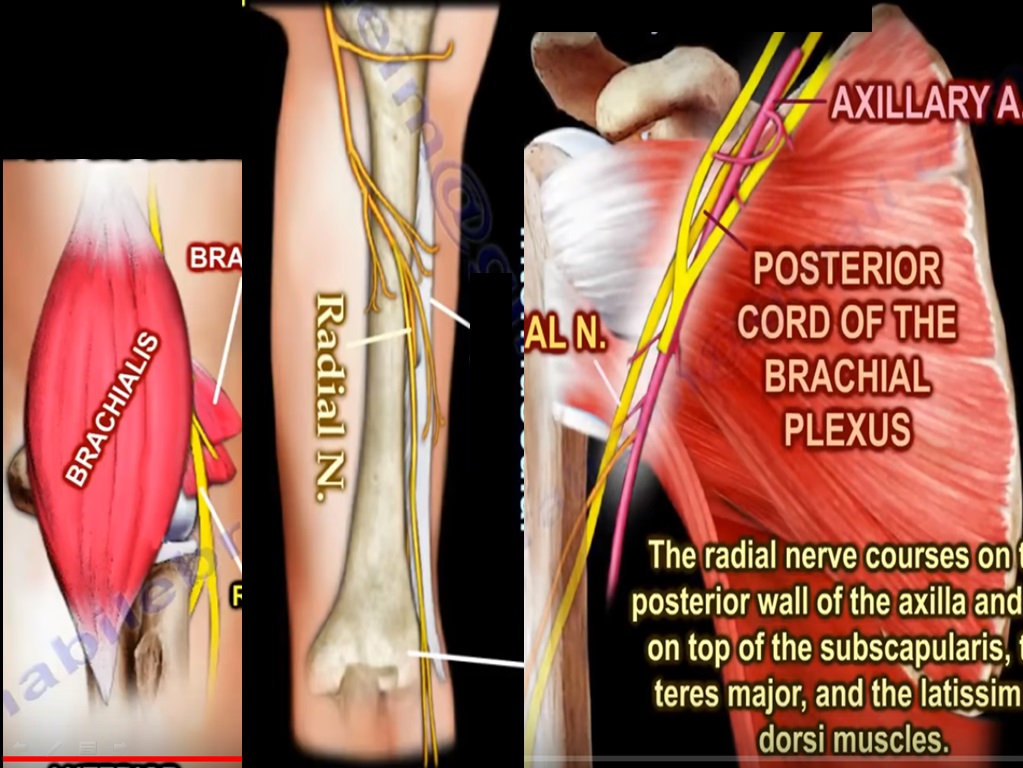
- It is a major peripheral nerve in the upper limb.
- It arises from the posterior cord of brachial plexus and contains fibres from nerve roots C5 to T1
COURSE
- It arises in the axilla posterior to axillary artery
- Traverses through the posterior wall of axilla and lies on top of 3 muscles – subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi
- It gives off 3 branches in the axilla
1.Branch to long head of triceps
2.Branch to medial head of triceps
3.Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm - Radial nerve exits the axilla inferiorly via the triangular interval with the profunda brachii artery, which is a branch of axillary artery
- The triangular interval is bounded by teres major proximally, long head of triceps medially and humeral shaft laterally.
- The Radial nerve then enter the upper arm between the long and medial heads of triceps and then runs through the spiral groove of humerus, which is a thin bare area of bone which lies in the upper 2/3 rd of back of humerus, between the lateral and medial heads of triceps
- Hence the safe zones of humerus posteriorly are
1.10 cm distal to the latetal acromion
2.10 cm proximal to lateral epicondyle
In the spiral groove radial nerve gives rise to 4 branches
1.Branch to medial head of triceps
2.Branch to lateral head of triceps
3.Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of arm
4.Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm - Then it passes through the lateral intermuscular septum and enters the anterior compartment of the arm atleast 7.5 cm above the elbow joint
- Anteriorly the nerve runs between brachialis and brachioradialis, anterior to the lateral epicondyle and this is the site for exposure of radial nerve anteriorly.
- It then gives off 3 branches to supply
1.Lateral part of brachialis
2.Brachioradialis
3.Extensor carpi radialis brevis - Radial nerve is vulnerable to injury below the spiral groove when there is fracture to distal third of humeral shaft which then leads to wrist drop
- At the level of lateral epicondyle the nerve divides into deep and superficial braches.
- After giving supply to the anconeus muscle the deep branch or the posterior interosseous nerve enters the extensor compartment of forearm between the two heads of supinator muscles.
- The area in which the posterior interosseous nerve passes through is called the Arcade of Frohse and is often a site for entrapment of the nerve
- The posterior interosseous nerve, which is a pure motor nerve, then supplies the muscles of the forearm- Extensor indicis, Extensor pollicis longus, Extensor pollicis brevis and Abductor pollicis longus
- Injury to the posterior interosseous nerve causes inability to extend the fingers or hitchike the thumb
And during the recovery, extensor digitorum is the 1st one to recover and extensor indicis is the last one to recover - The superficial radial nerve runs deep to the brachioradialis muscle and continues until about 5 cm above the wrist where it emerges from underneath brachioradialis piercing the deep fascia and lying between the brachioradialis and the extensor carpi radialis longus and then descends towards the anatomical snuff box.
- It also gives sensory supply to majority of dorsum of hand
Wartenbergs syndrome
- Entrapment of superficial branch of radial nerve above wrist and is manifested as pain at about 8 cm proximal to radial styloid
Leave a Reply