Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
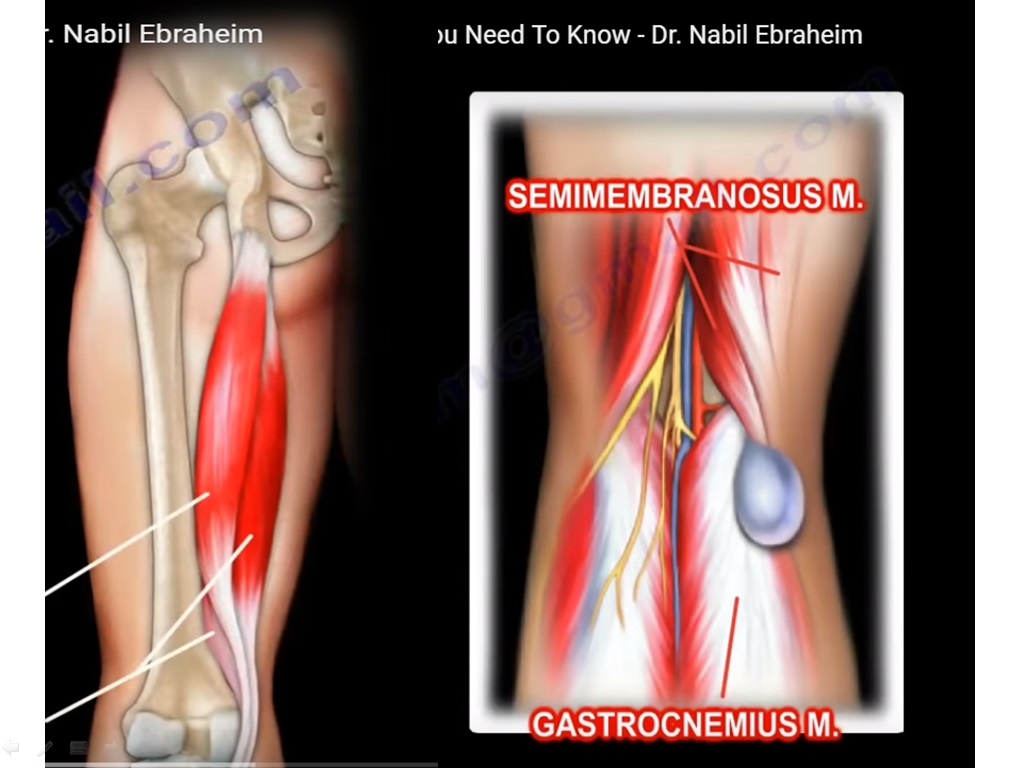 Anatomy of Semimembranosus
Anatomy of Semimembranosus
One of the 3 muscles that make up the hamstring. The other 2 are , semitendinosus and biceps femoris
Origin
- Upper lateral part of ischial tuberosity
Insertion
- Back of the posterior surface of the medial tibial condyle
Nerve supply
- Sciatic nerve
Action
1.Flexion of knee
2.Extension of hip
3.Medial rotation of tibia
Conditions associated
1. Bakers cyst
- Cyst located between semimembranosus and medial gastrocnemius muscles
- Commonly caused by knee arthritis or a meniscal tear
- It is connected to the knee joint through a valvular opening
- Knee effusion from intraarticular pathology allows the fluid to go through the valve into the cyst in one direction
2.Approach to posteromedial fracture of tibial plateau
- Through an incision between semimembranosus and medial gastrocnemius
Leave a Reply