Courtesy:Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
- Crush syndrome occurs due to crushing accidents such as those seen in war zones, industrial accidents, and natural disasters, drug overdose or positioning in long surgery.
- When the muscle is crushed, this results in muscle necrosis (rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinuria).
- This crush injury causes muscle breakdown and the toxic muscle cell components and electrolytes are released into the blood stream causing third spacing and acute renal failure.
- Crushing of the limbs or the trunk can create a very harmful side effect known as crush syndrome.
- Crush injuries occur in the lower extremities than the upper extremities and the trunk.
- Crush injuries are commonly seen with injury due to earthquakes. Some of these patients will have acute renal failure.
- Some patients will require dialysis and fasciotomies.
- The three main conditions associated with crush syndrome will be local muscle damage, organ dysfunction and metabolic abnormalities.
- If not treated promptly, the patient could die within days.
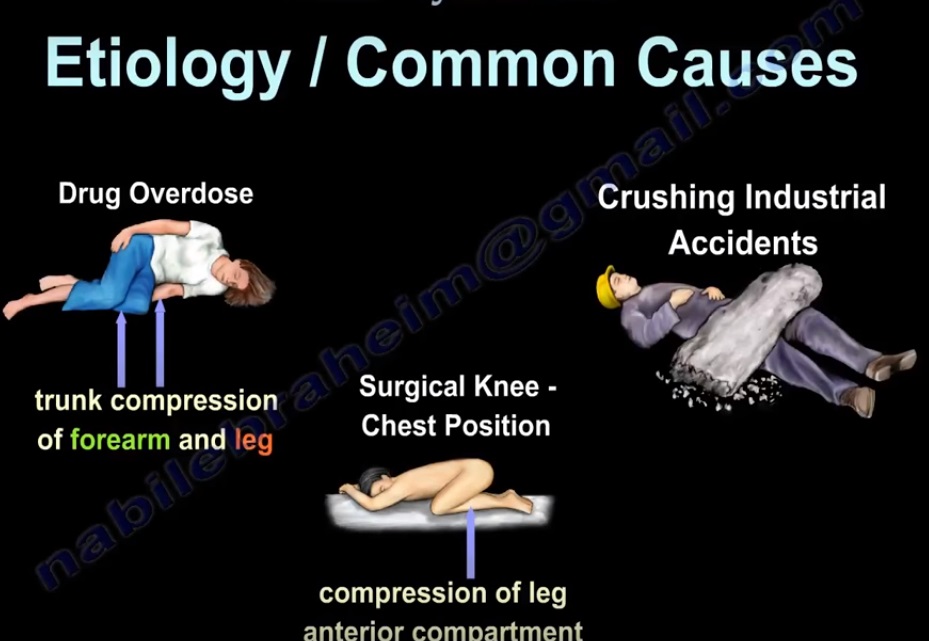
- Etiology/ common causes
- 1.Drug overdose: trunk compression of forearm and leg.
- 2.Surgical knee chest position: compression of leg anterior compartment.
- 3.Crushing industrial accidents.
Pathogenesis
- Crushing injury/limb compression – soft tissue injury – ischemia – muscle necrosis and compartment syndrome
- Muscle necrosis: 1. Rhabdomyolysis- myoglobinuria and/or myoglobinemia- acute renal failure
- 2. Third space fluid loss- hypovolemic shock- acute renal failure
- 3. Metabolic abnormalities- ventricular fibrillation
- 4. Metabolic acidosis and hyperkalemia will lead to cardiac arrhythmia (ventricular fibrillation)
- 5. Disseminated intravascular coagulation – coagulation deficiency
- 6. Other complications (compartment syndrome): pulses may not be affected Microcirculation is affected.
- The muscle is swollen with irreversible damage to the muscles and the nerves.
Treatment
- A multidisciplinary approach involving the medical and surgical team is needed.
- Medical management •Fluid replacement: ideal fluid is normal saline •Ventilatory support •Correction of metabolic acidosis •Consider dialysis Surgical management •Emergency fasciotomy
- Crush syndrome can occur even if the patient is trapped less than one hour.
- It can happen without fracture and even if good pulses are felt. Early fasciotomy must be done.
- Debridement of necrotic tissue
- Consider delayed VAC application and skin grafting.
- Mortality can be early due to hypovolemia and hyperkalemia or late due to multiple organ failure and sepsis.
- Example of a patient with crush syndrome to the shoulder, arm, buttock, and thigh
- Measuring the pressure. Very high pressure (71) •Fasciotomies and debridement of the dead muscles •Application of VAS and partial closure as the condition of the patient permits.
Leave a Reply