Courtesy: Saqib Masud FRCS,
John Davies FRCS
Anterior approach to hip
The anterior approach also known as the Smith Peterson approach gives a safe access to the hip joint. They also provide access to the pelvis for pelvic osteotomy.
Patient is positioned supine, if an osteotomy is performed then a sand bag is placed beneath the ipsilateral buttock.
This approach can also be used for total hip replacement, special traction tables are used in such situations.
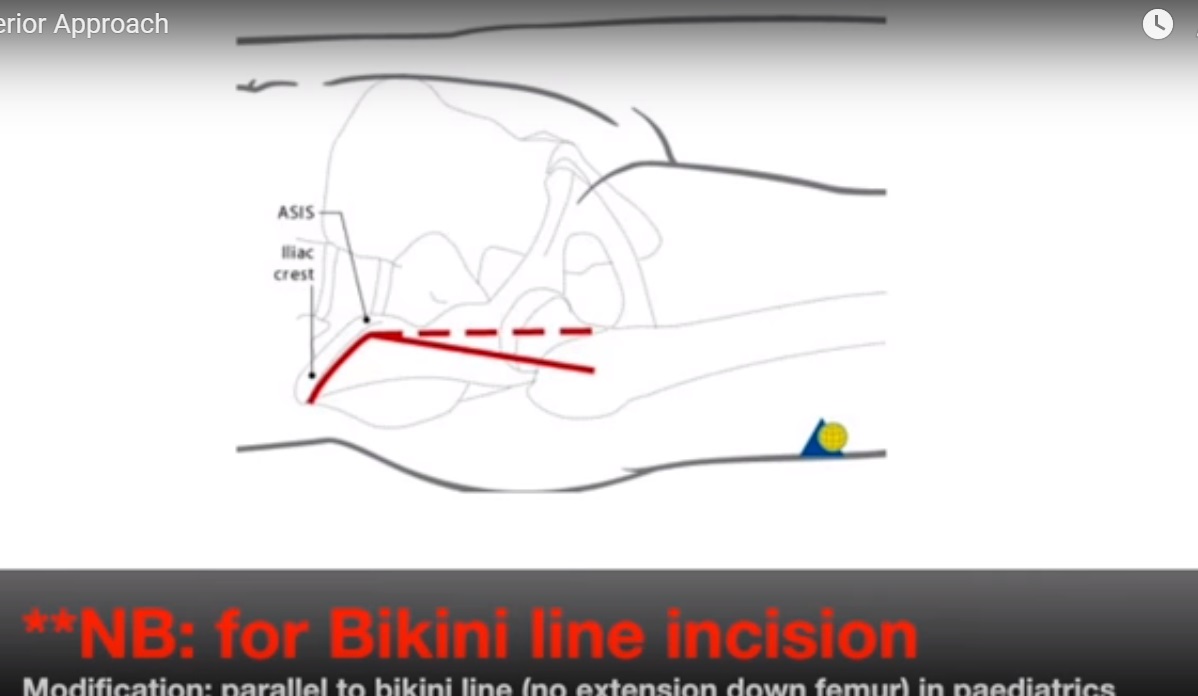
Landmarks : iliac crest, ASIS, Femoral shaft.
An incision is made over the anterior half of the iliac crest down to the ASIS and this is curved vertically downwards for a further 8-10 cms.
This approach uses the internervous plane between the superior gluteal nerve ( which supplies tensor fascia lata and gluteus medius) and femoral nerve (which supplies sartorius and rectus femoris).
The gap between the two structures is identified and to help with this the leg is externally rotated to make the sartorius more prominent. Best place to identify the Interval is 5-7cms below the ASIS. The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is at risk at this stage as it pierces the deep fascia 2.5cms below the ASIS.
Make an incision on the medial aspect of the tensor fascia lata and stay within it’s fascial sheath- this way you can protect the nerve. The tensor fascia lata is retracted laterally and sartorius with the nerve is retracted medially. Beware of the ascending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery which lies in the interval.
Deep dissection is performed between gluteus medius laterally and rectus femoris medially. Detach rectus femoris from both of its origins, the direct head from the ASIS and the reflected head from the superior lip of the acetabulum. At this point the femoral nerve and artery are at risk as they lie medial to the rectus femoris within the femoral triangle. The anterior hip joint capsule is then exposed and iliopsoas is retracted medially. The leg is the adducted and fully externally rotated to put the capsule on a stretch for capsulotomy and then the hip is dislocated. This approach is enlarged with local measures by releasing the origins of tensor fascia lata,sartorius and gluteus medius and minimus. Extensile exposures include proximal extension over the iliac crest to expose the inner and outer walls of pelvis. Distally it can be extended along the anterolateral aspect of thigh to expose the entire shaft of femur.
Leave a Reply