Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
- Osteoclast is a large multinucleated cell. It has 15- 20 nuclei.
- Its origin is from the fusion of macrophages /monocytes.
- As many as 50 of cells fuse to form a giant osteoclast.
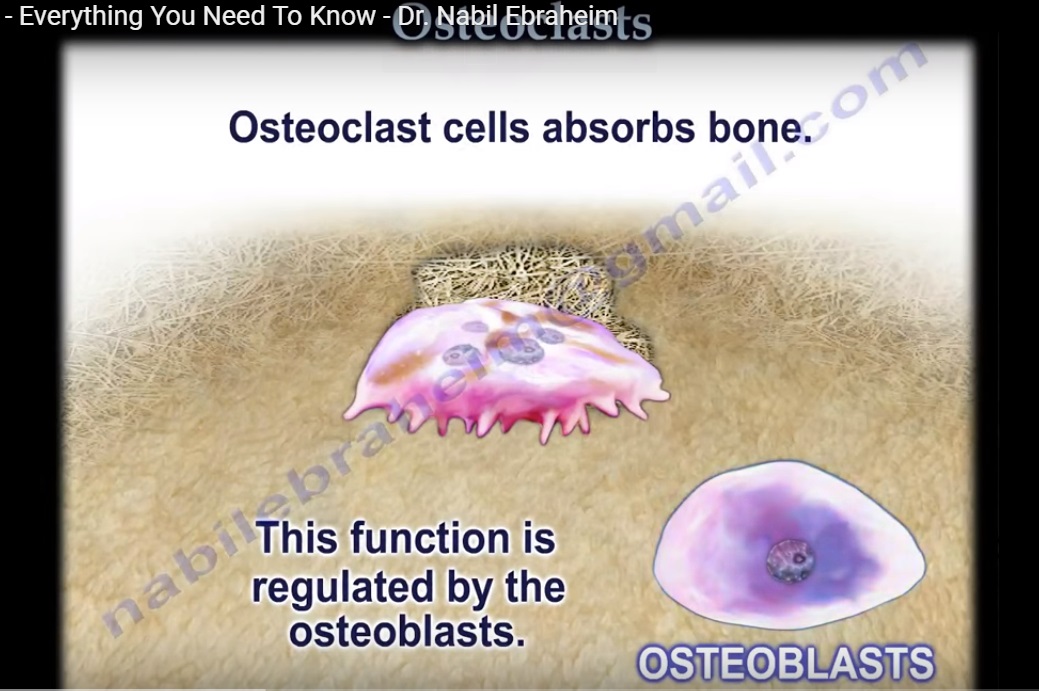
- Osteoclast absorbs bone. Its function is regulated by osteoblast.
- Life span is of few days. It may take 100-150 osteoblast to replace the bone that has been removed by one osteoclast. It has lots of mitochondria
- Osteoclast is found against the bone surface in a hollow depression called howship lacunae. The howship lacunae is the site of bone resorption where the ruffled border meets the bone surface.
- It secretes 2 enzymes
- Cathepsin- it absorbs the osteoid . Mutation of the gene that codes the enzyme causes pycnodystosis.
- TRAP- dissolves the hydroxyappatite crystals.
How resorption occur?
- Osteoclast attaches to the bone by 2 proteins.
- Integrin is on the osteoclast and Vitronectin is on the bone.
- They lock to each other creating a sealing zone.
- Then osteoclasts create an acidic environment by producing hydrogen atoms through carbonic anhydrase , which demineralise the bone.
- This occurs by sealing the space and lowering the pH level, thus increasing the solubility of the hydroxyappatite crystals.
- Matrix is degraded by the cathepsin B.
What is clear zone?
- Osteoclast bind to bone through cell attachment utilizing anchoring protein. Clear zone is cytoplasmic area presenting the adhering plasma membrane.
- Osteoclast has 2 centres on its surfaces
1.Calcitonin receptor- inhibits osteoclast
2. RANK receptors- stimulate osteoclast. RANK ligand comes from osteoblast and tumor cells. - RANK ligand which bind to osteoclast will stimulate the differentiation and activation of osteoclast and increase bone resorption.RANK ligand function is inhibiting osteoprotegerin[OPG].The balance between OPG and RANK L is important.
Osteoclast inhibition
1. Calcitonin
2. IL-10
3. Denosumab
4. Bisphosphonates
Osteoclast stimulation and activation
1.RANK L
2.IL-1
3. Macrophage colony stimulating factor
Leave a Reply