Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURE CLASSIFICATION
Femoral neck fractures can occur as a result of low energy trauma in the elderly.
- can also occur due to high energy trauma such as with falls or motor vehicle accidents.
- can occur in older as well as younger patients, and in these cases you need to apply the ATLS protocol
- can also occur due to insufficiency fractures. This occurs due to weak bones, because of osteoporosis or osteopenia. The patient will have groin pain pain with axial compression and the X-ray may be normal (helpful in diagnosing insufficiency fracture).
- can also be a stress fracture due to overuse and more loading on the hips, stress fractures may occur in athletes, ballet dancers, or military recruits.
ANATOMIC CLASSIFICATION
1. Subcapital – common
2. Transcervical
3. Basicervical
The subcapital fracture has two classifications:
a) Garden classification
b) Pauwel’s classification.
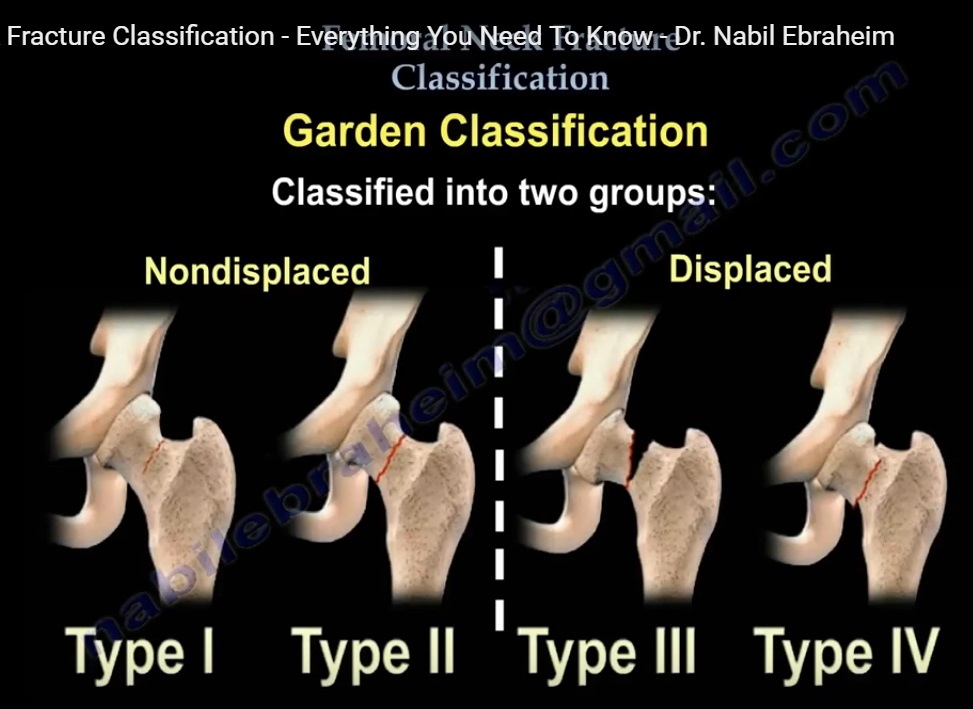
GARDEN CLASSIFICATION
Classifies the fracture according to the amount or degree of displacement. It relates the amount of displacement to the risk of vascular disruption. This classification applies to the geriatric and insufficiency fractures.
It can then be classified into two groups.
A) Non displaced (type I and type II)
B) Displaced (type III and type IV)
-Type I is incomplete and impacted in valgus.
-Type II is a complete fracture and nondisplaced on at least two planes (anteroposterior & lateral).
-Type Ill is a complete fracture and partially displaced. The trabecular pattern of the femoral head does not line up with the acetabular trabecular pattern
-Type IV fracture is completely displaced with no continuity between the proximal and distal fragments. The trabecular pattern of the femoral head remains parallel with the acetabulum trabecular pattern.
THE PAUWEL’S CLASSIFIATION
Classified into three fracture types. It classifies the fracture according to the orientation and direction of the fracture line across the femoral line. it related to the biomechanical stability. The more vertical the fracture, the more sheer forces and the more the complication rate.
1. Type I is stable and has an obliquity ranging from 0-30 degrees.
2. Type lI is less stable and have an obliquity ranging from 30-50 degrees.
3. Type III is unstable and has an obliquity between 50-70 degrees or more.
-As the fracture progresses from Type I- Type III, the obliquity of the fracture line increases.
-As the fracture line becomes more vertical the sheer forces increase and the instability increases.
-A horizontal fracture is good and stable while a vertical fracture is bad and unstable.
- The more displaced the fracture, the more disruption of the blood supply and the chance of avascular necrosis and nonunion (can occur in about 25% of displaced fractures).
- If nonunion occurs in a younger patient, you may help the patient by doing a subtrochanteric osteotomy to reorient the fracture line from vertical to horizontal (will help the Fracture healing).
Femoral Neck Fractures Associated with Femoral Shaft Fractures
The typical neck fracture is vertical and non-displaced it may require internal rotation view xrays to see this hip fracture (fracture could be missed). Treatment of this fracture is to fix the femoral neck fracture first, followed by the femoral shaft fracture. The usual combination is parallel screws in the femoral neck and a retrograde femoral rod for the fractured femur.
PIPKIN TYPE III FRACTURE
Fracture of the femoral head + dislocation of hip + fracture of femoral neck
Try to avoid reduction of the hip dislocation by closed means
May want to do open reduction of the hip dislocation especially if the femoral neck fracture is not displaced
STRESS FRACTURES
More common in females due to the female athletic triad (1. Amenorrhea 2. Eating disorders 3. Osteoporosis/ Osteopenia). Types
A) Tension fracture.
The fracture or callus is present on the superior aspect of the femoral neck. Adult bone is weak in tension, so stress fracture of the femoral neck needs to be fixed. This should be an emergency operation before the fracture displaces. A female runner with groin pain can indicated a stress fracture. Get an MRI the fracture Will probably need to be fixed.
B) Compression fractures
The compression or callus is present on the inferior aspect of the femoral neck.
a) if the compression fracture is less than 50% across the neck, then the fracture could be stable and you can do protected crutch ambulation.
b) if the fracture is more than 50% across the neck, then the fracture is unstable and you will do an ORIF.
Leave a Reply