ANATOMY OF TIBIALIS ANTERIOR MUSCLE
The leg has four muscle compartments
- Anterior
- Lateral
- Superficial posterior
- Deep posterior
Anterior compartment
- Nerve within the compartment- Deep peroneal nerve
- Muscles include : Tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus
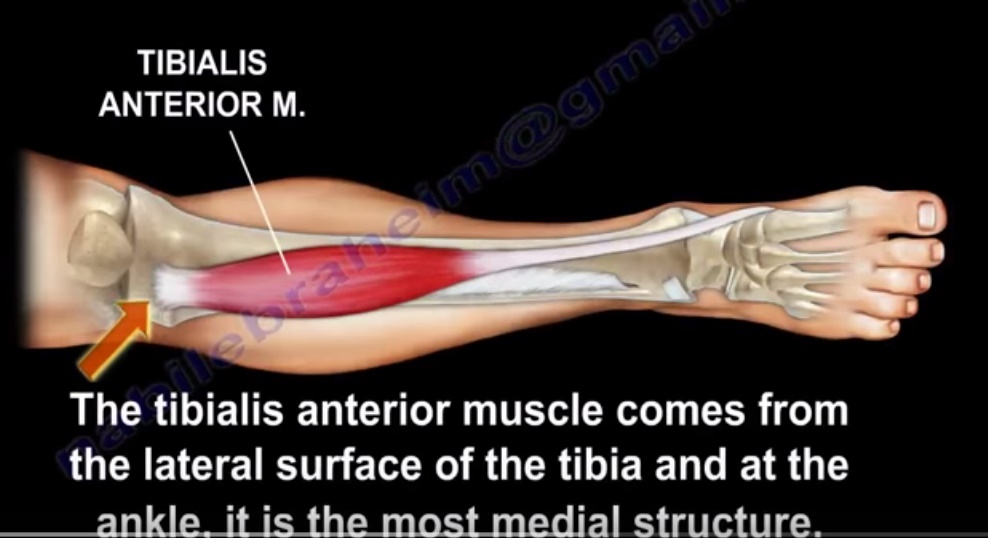
Origin
- Upper half and lateral condyle of tibia
Insertion
- Medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bone of foot
Course
- The tendon of tibialis anterior along with other extensor tendons pass under the extensor retinaculum
Structures of anterior compartment
- Tibialis anterior
- Flexor hallucis longus
- Extensor digitorum longus
- Peronius tertius
- Anterior tibial artery
- Deep peroneal nerve
Nerve supply of tibialis anterior muscle: Deep peroneal nerve
INTERRUPTION OF NERVE SUPPLY
- Pelvic fracture affecting L4-L5 root
- Posterolateral disc herniationL3,L4
- Foraminal disc herniationL4-L5
- Sciatic nerve injury
FUNCTION OF TIBIALIS ANTERIOR
- Dorsal flexion of ankle
- Invertion of hind foot
- Tibialis anterior dorsiflexes the foot in preparation for heel strike during the last swing phase of the gait and it eccentrically contracts after heel strike to slow progression to foot flat.
RUPTURE OF TIBIALIS ANTERIOR TENDON
- Cause loss of dorsiflexion of ankle
- May occur due to laceration
- May also be a closed rupture
Closed rupture
- It occurs due to strong eccentric contracture in young patients or attenuation rupture in elderly who have diabetes , inflammatory arthritis or from steroid injections.
Presentation
• Difficulty clearing the foot during the gait with chronic rupture
• In acute rupture, will hear a POP and there will be swelling of the anterior ankle
1. Foot drop
2. Steppage gait
3. Pseudo tumour
4. Anterior ankle pain
5. Weak dorsiflexion
6. No tendon is felt in resisted dorsiflexion
TREATMENT
• PARTIAL TEAR: CAST APPLICATION
• COMPLETE TEAR: AFO in low demand patients , however surgical repair proves to be successful in elderly
SURGERY
BEST CHOICE
• Acute repair , end to end repair when the tendon is normal
• In chronic rupture do autograft (EHL) or allograft
Important points
• When foot drop occurs in compartment syndrome it is due to tibialis anterior
Charot-Marie-Tooth disease
(peroneal muscular atrophy) the affected muscles become weak:
– Tibialis Anterior
– Peroneus Brevis
– Intrinsic muscles of the hand and foot
The weak tibialis anterior muscle is overpowered by the unaffected peroneus longus muscle, bringing
the first ray into a plantarflexed position.
Courtesy: Prof Nabile Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Leave a Reply