Courtesy: Prof Nabile Ebraheim, Chairman, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Trauma, University of Toledo, Ohio, United States.
Anatomy of biceps femoris
• The biceps femoris is a muscle of posterior thigh.
• The biceps femoris is one of the three flexor muscle of the posterior thigh.
Hamstrings muscles(there are three):-
1. Biceps femoris
2. Semitendinosus
3. Semimembranosus
• The ischial tuberosity is divided by a transverse ridge into an upper quadrangular portion and a lower triangular portion and each portion is divided into medial and lateral parts.
The biceps femoris has two heads of origin:-
• The long head of the biceps femoris arises from the upper and medial part of the neck of the ischial tuberosity.
• The short head of the biceps femoris arises from the lateral lip of the linea aspera on the posterior femur
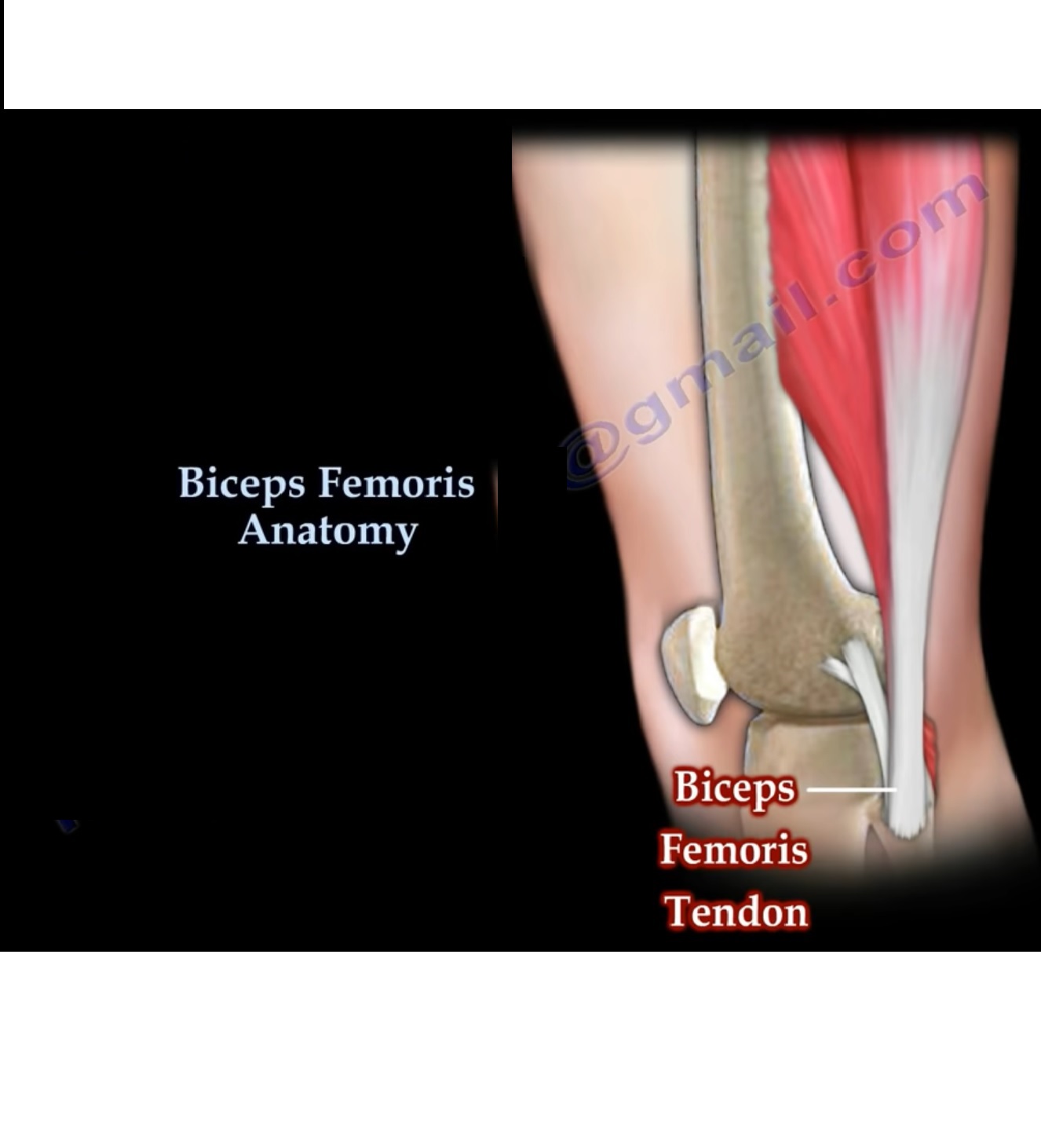
• Both heads of the biceps femoris are inserted into the head of the fibula along with the lateral collateral ligament and the popleteo fibular ligament.
The insertion of the structure from anterior to posterior on the fibular head:-
1. Lateral collateral ligament
2. Popleteofibular ligament
3. Biceps femoris tendon-most posterior structure on the proximal fibula
Innervation:
• The long head is innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve(L5, S2)
• The sciatic nerve starts in the lower back and runs through the buttock and lower limb.
• In the thigh ,the tibial part innervates the long head of the biceps femoris muscle, while the peroneal part innervates the short head .
• The tendon of biceps femoris muscle forms the lateral hamstring.
Blood supply:
• The biceps femoris muscles vascular supply is derived from the perforating branches of the inferior gluteal artery, the profunda femoris artery, and the popliteal artery.
Function:-
• The biceps femoris muscle flexes the knee joint and laterally rotates the knee joint when the knee is flexed.
• The biceps femoris also extends the hip joint(long head only).
Hamstring injuries: –
• The upper medial portion of the ischial tuberosity is where the insertion of the biceps femoris and semitendinosus located.
• Muscle strain or tear of the muscle can occur in sports that require rapid acceleration and deceleration.
• Eccentric loading may cause these injuries.
• Injury usually involves the myotendinous junction approximately 12 cm distal to the ischium.
• Complete rupture or avulsion from the ischial tuberosity may also occur. These complete ruptures need repair.
• If not repaired the rupture will lead to significant functional impairment which is more profound during vigorous activity.
Sciatic nerve injuries:-
• High sciatic nerve lesions can mimic peroneal neuropathy at the fibular head.
• Patient will have foot drop and emg abnormalities in the short head of the biceps femoris muscle.
• In the presence of EMG changes in the short head of the biceps, the lesion is not from injury to the common peroneal nerve at the fibular head, but from injury to the sciatic nerve
Leave a Reply