Courtesy; Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
The bone has two important cells – osteoclast and osteoblasts.
- Osteoclasts are irregular shaped giant cells that break down or reabsorbs bone.
- Osteoblasts are cells that are responsible for new bone formation.
- Osteoclast arise from either macrophages or monocytes .
- Monocytes fuse together to form multinucleated osteoclast cells.
- Osteoclast cells have a ruffled border which touches the bone and increases the surface area for absorption of bone.
- Osteoclast bind to the bone via integrin [protein].
- Vitronectin helps to attach the osteoclasts to the bone.
- The bone is absorbed at the howship lacunae .
- As the ruffled border of the osteoclast contacts the bone it secretes acids that lowers the pH level and the osteoclast then absorbs the mineralized bone matrix.
- Cathepsin K is an enzyme that removes the bone at the ruffled border.
- Osteoclast secrete tartate resistant acid phosphates.
- Osteoclasts are unable to absorb unmineralized osteoid.
- There are proteins that interact with the osteoclasts and osteoblasts to control bone reabsorption.
- The osteoclast has RANK receptors on its surface.
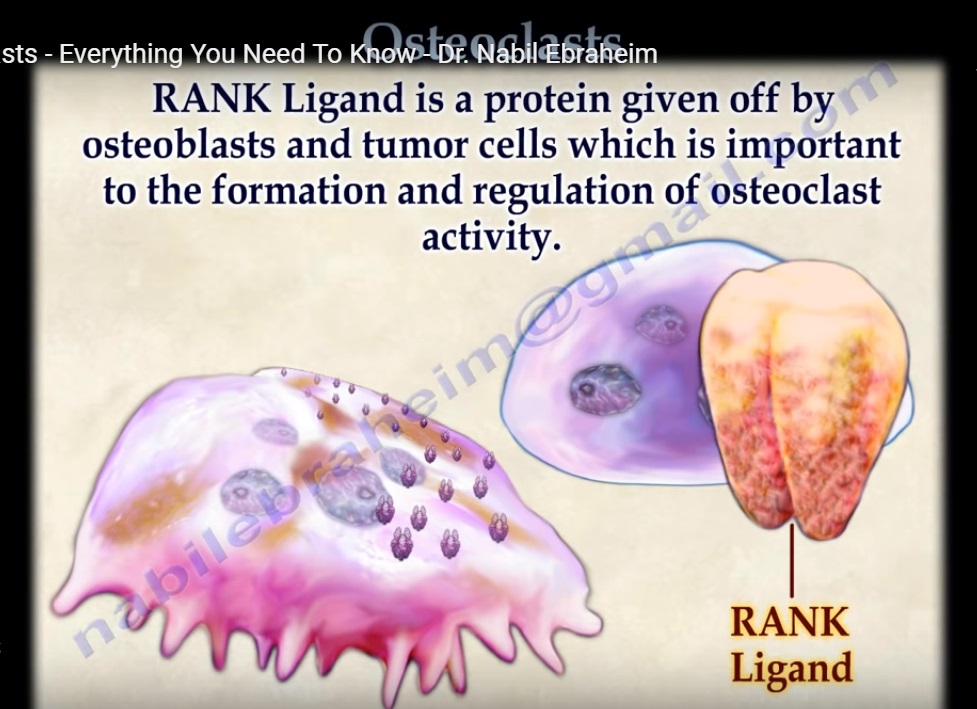
- RANK ligand is a protein given off by the osteoblasts and tumor cells which is important to the formation and regulation of osteoclast activity.
- RANK ligand proteins interact with the RANK receptors on the surface of the osteoclast.
- OPG is another protein that is secreted by the osteoblasts that block the binding of RANK ligand to RANK..
- The OPG protein is a decoy that stops the osteoclast from differentiation, fusion and activation , which causes decrease in bone reabsorption and destruction. This action of blocking the binding of RANK ligand to RANK reduces osteoclast activity. Excessive amounts of RANK ligand leads to more osteoclasts and greater bone loss.
Osteoclast inhibition
- Calcitonin- there is a receptor for calcitonin on the osteoclast surface that inhibits bone resorption.
- Bisphosphonates- prevents formation of the ruffled border and may cause apoptosis
- IL- 10- suppress osteoclast activity.
- OPG- blocks the binding of RANK ligand to RANK.
- Transforming growth factor beta– inceases OPG
- Estrogen- decreases RANK ligand expression by the osteoclast. decreases activity of the adenylyl cyclase
Osteoclast activation
- Parathyroid hormone related protein
- Secreted by many cancer cells including breast cancer. Utilizes adenyl cyclase. Bind to a receptor of the osteoblast to produce RANK ligand.
- 1,25 dihydroxy vit D- increases production of RANK ligand
- IL_6-tumors especially myeloma
- Prostaglandin E2-activate adenylyl cyclase
GOOD