Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
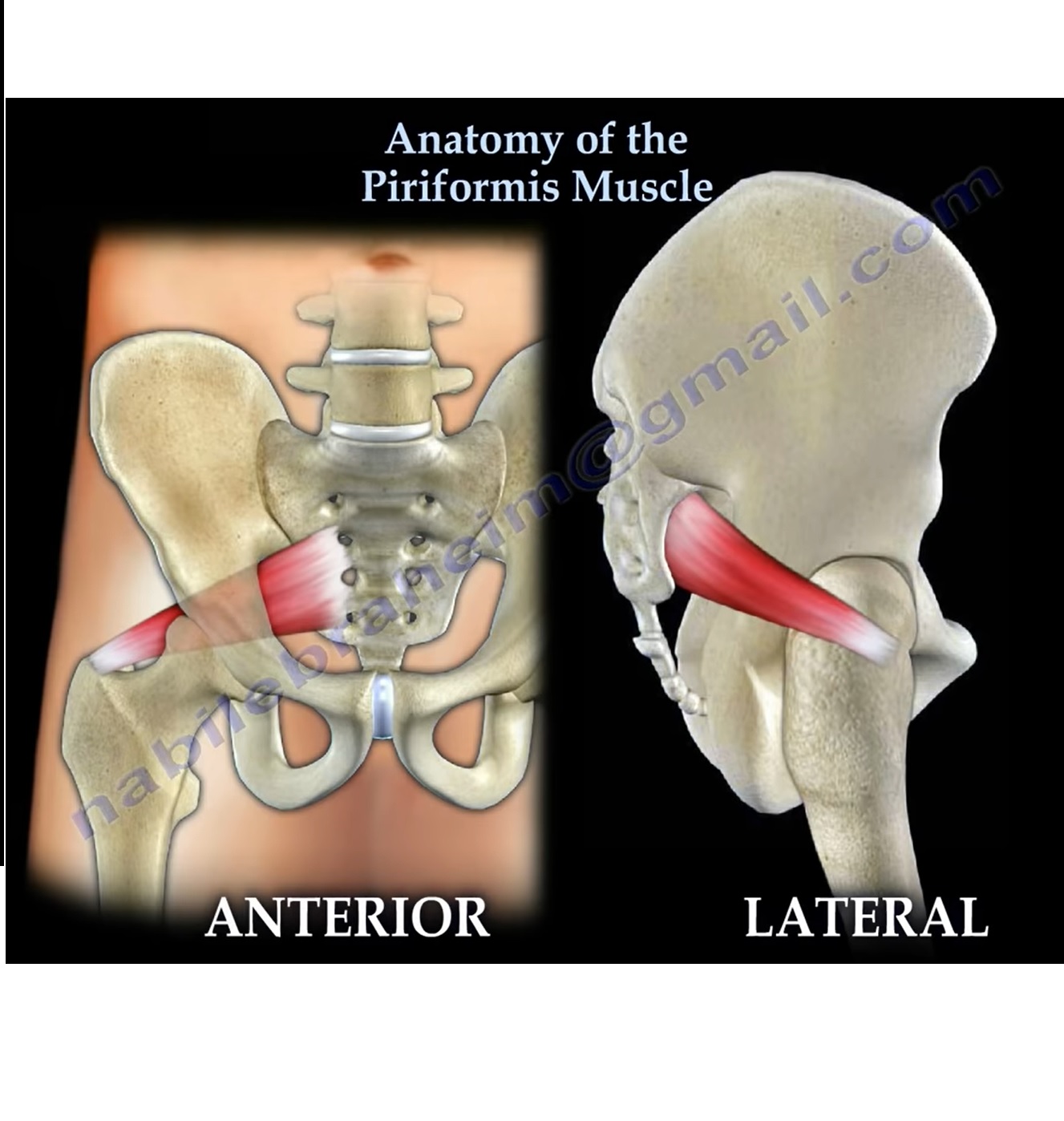
ANATOMY OF PIRIFORMIS MUSCLE
• The sciatic nerve may become compressed or irritated by the piriformis muscle
• The piriformis muscle is one of the six lateral hip rotators
• The nerve to piriformis is a nerve that innervates the piriformis muscle(L5,S1,S2)
• Normally sciatic nerve passes beneath the piriformis muscle
ORIGIN AND INSERTION
• The piriformis muscle arises from the sacroiliac joint capsule at the anterior surface of the lateral process of the sacrum and gluteal surface of the ileum at the margin of the greater sciatic notch
• The muscle is inserted to the superior border of greater trochanter
• Because the piriformis muscle also arises from the capsule of the SI joint, the association of piriformis muscle syndrome and SI joint pain exists
• The piriformis muscle functions to laterally rotate the hip as well as abducts the hip if it is flexed
• Be aware of possible anatomical variations of the sciatic nerve in relationship to the piriformis muscle
• There are 4 types of variation:
• The sciatic nerve is composed of the tibial and peroneal divisions which are usually bound together but sometimes may divide as they pass the piriformis muscle
Relation of the sciatic nerve to the piriformis muscle:
1. Normal relationship with the sciatic nerve passing beneath piriformis muscle
2. Piriformis divided in to two parts with the peroneal division of the sciatic nerve passing between the two parts of the muscle
3. Peroneal division of the sciatic nerve passes over the muscle and the tibial division passes beneath the undivided piriformis muscle
4. The entire nerve passes through the divided piriformis muscle
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF PIRIFORMIS MUSCLE
- The piriformis fossa is the proximal entry point for most intramedullary rod placement
Piriformis syndrome
Diagnosis of piriformis syndrome-
- High index of suspicion
- Patient history and exam
- EMG and bone scan not very helpful
Symptoms:
- Occasionally develops from blunt trauma to the buttocks
- Localised buttock pain increased by sitting or driving
- Tenderness in the sciatic notch
- Pain increased by bicycling or running in young individuals
- Radicular symptoms with pain and paresthesia, however it is not common
- Pain may be present when palpating directly deep in to the area of greater sciatic notch
Provocative test:
Lasegue’s Maneuver
- Reproduction of the pain by the hip being flexed to 90 degree and the knee extended
The sciatic nerve is compressed by the piriformis muscle, fibrous bands or by vascular anomalies
Diagnosis
- MRI- Enlarged piriformis, anomalies of the vessels, Compression of the nerve
- Diagnostic injection is helpful
Treatment
- Aquatic therapy
- Physiotherapy
- NSAIDs medication
- Injections
- Surgical release of the piriformis muscle and decompression of the sciatic nerve is the last resort
This is an very important muscle and preservation of this muscle has been known to help in reducing posterior dislocations of the Hip Joint.
References:
1.. Piriformis and obturator internus morphology: a cadaveric study. Clinical Anatomy 01/2011
24(1):70-6.
2.. INCIDENCE OF PIRIFORMIS TENDON PRESERVATION ON THE DISLOCATION RATE
OF TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT FOLLOWING THE POSTERIOR APPROACH,
by Charbel D. MOUSSALLEM,Fadi A. HOYEK and Jean-Claude F. LAHOUD
in the Lebanese Medical Journal 2012 – Volume 60 (1) 19
Dr.K.Mohan Iyer,Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon,Bangalore,India