Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim
- The median nerve originates from the lateral cord and the medial cord of the brachial plexus.
- The median nerve runs down the arm where it passes on the medial side of arm between the brachialis and the biceps brachii.
- The median nerve does not give branches in the axilla or in the upper arm.
At the elbow region, the median nerve moves into the area of the cubital fossa. Structures at the elbow from medial to lateral:
•Median nerve
•Brachial artery
•Biceps tendon
At the cubital fossa, the median nerve gives branches to four muscles
1.Pronator teres
2.Flexor carpi radialis
3.Palmaris longus
4.Flexor digitorum superficialis
- The median nerve leaves the elbow region and enters the forearm between the two head of the pronator teres muscle. The median nerve branches as it course through the forearm. The anterior interosseous nerve branches out to innervate the muscles of the deep group of the anterior compartment of the forearm.
- The anterior interosseous nerve gives branches to the lateral half of the flexor digitorum profundus, the flexor pollicis longus and the pronator quadratus. A patient with paralysis of the anterior interosseous nerve will be unable to give the OK sign.
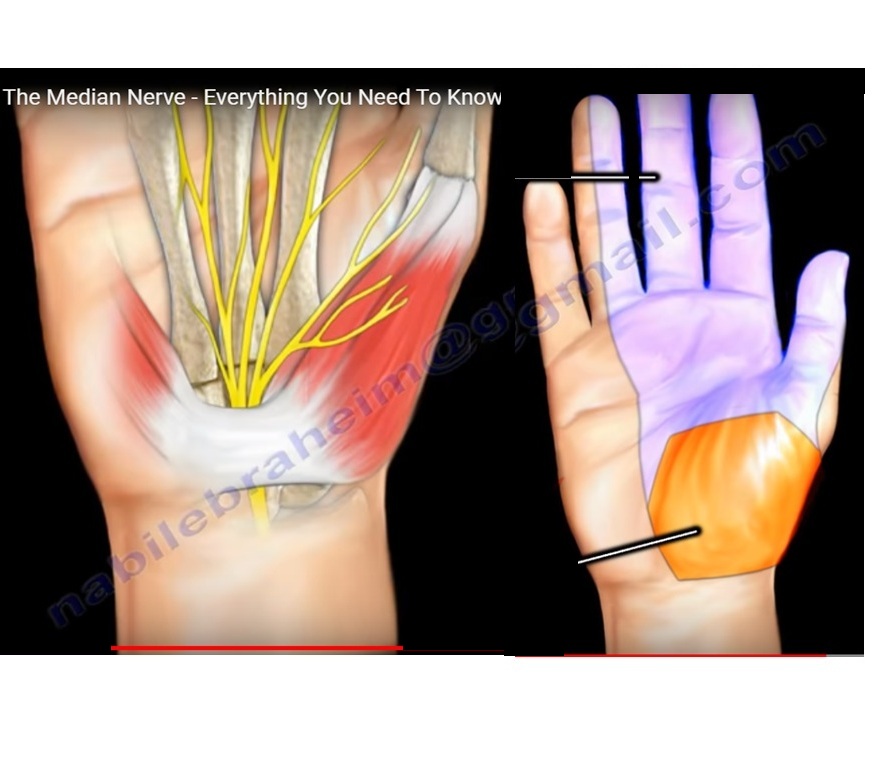
- The median nerve gives the palmar cutaneous branch about 3 cm above the wist which gives innervation to the radial part of the palm. It descends over the flexor retinaculum to supply the palm of the hand.
At the wrist the median nerve becomes superficial between the flexor carpi radialis and the palmaris longus and then enters the carpal canal under the transverse carpal ligament. The median nerve ends in the carpal tunnel by giving the recurrent thenar motor branch and dividing into two terminal divisions which are radial and ulnar. After passing through the carpal tunnel the first branch of the median nerve is called the recurrent thenar motor branch. The recurrent thenar motor branch gives innervation to the abductor pollicis brevis, the superficial branch of the flexor pollicis brevis, and the opponens pollicis muscles.
- The radial division of the median nerve then divides into three digital branches which supply the two sides of the thumb and the lateral side of the index finger and also supplies the first lumbrical.
- The ulnar division of the median nerve divides into common digital nerve that supplies the second and third web space providing sensation to the adjacent sides of the index and middle finger and the middle and ring finger. The ulnar division also gives innervation the second lumbricals.
- The median nerve innervates the skin on the palmar side of the thumb, the index finger, the middle finger and half of the ring finger.
- The median nerve may become compressed as it passes through the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused when there is pressure in the carpal tunnel that compresses the median nerve, causing the nerve to function improperly.
Leave a Reply