Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim
The biceps muscle has two tendon in the shoulder:
- Long head
- Short head
Pain at the front of the shoulder commonly occurs from conditions affecting the long head of the biceps tendon. The biceps tendon arises from the superior labrum at the top of the glenoid. It passes underneath the transverse humerla ligament in the groove between the lesser and the greater tuberosity of the humerus.
The biceps tendon ends by inserting into the proximal radius at the elbow region.
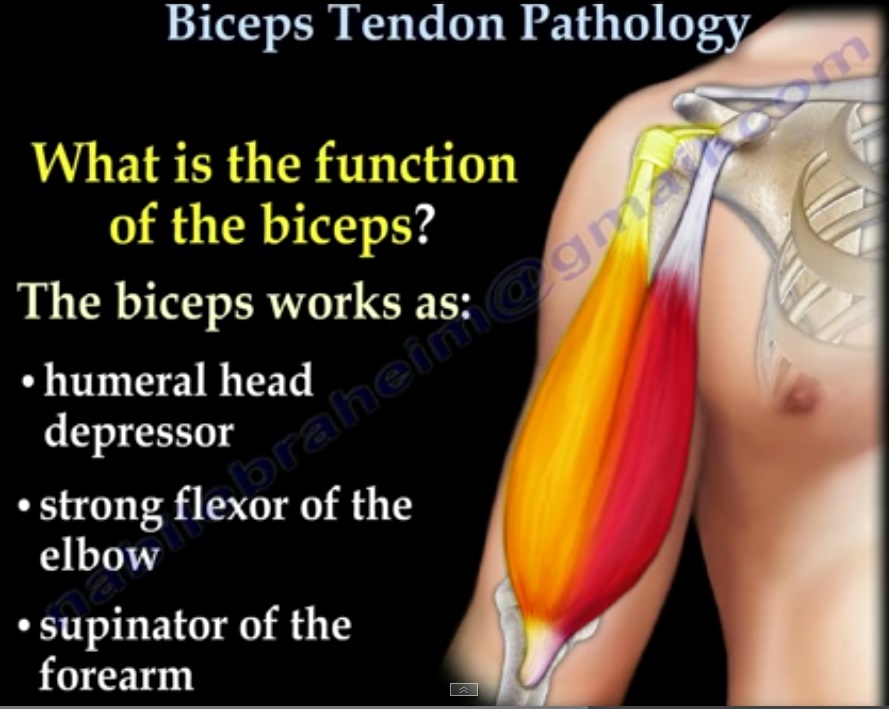
What is the function of the biceps?
- Humeral head depressor
- Strong flexor of the elbow
- Supinator of the forearm(also called supinator longus)
Conditions affecting the biceps
Biceps tendonitis
It is inflammation or irritation of the upper biceps tendon. Recurrent microtruama to the tendon, overusue and repetive overhead activities, leads to biceps tendonitis. These activities include sports such as baseball, tennis, swimming, or lifting weights. Usually occurs in association with other shoulder problems as shoulder impingement, tears of the glenoid labrum, shoulder instability, shoulder joint arthritis and rotator cuff tears. Shoulder impingement is a main cause of biceps tendonitis.
The soft tissue between the humeral head and the acromion can be pinched or squeezed with arm movements.
Symptoms
•Anterior shoulder pain
•Bicipital groove tenderness
Speed test
The arm is supinated and the elbow is extended. The patient is asked to actively flex the shoulder while the examiner is applying resistance to the movement. Tenderness over the bicipital groove indicates tendonitis of the long head of the biceps.
Treatment
Conservative treatment
- Rest
- Ice
- Physical therapy
- Steroid injections (around the tendon, not through the tendon).
Surgical treatment
- If the condition does not improve with conservative treatment. Biceps tenotomy: damaged biceps tendon is released form its attachment. Cut the biceps tendon and let it fly. Done in elderly and low demand patients. Patients may have subjective cramping. May result in a popeye bulge. Damaged section of the biceps is removed. Remaining tendon is reattached to the upper bone (humerus). Usuallyu done for high demand patients
Biceps tendon rupture
- The biceps tendon may rupture at the top of the bicipital groove or it may rupture at the radial tuberosity in the elbow
Proximal rupture
- At the bicipital groove. Muscle moves towards the elbow (popeye). There is minimal loss of function with a long head rupture because the short head of biceps remains attached to the coracoid process.
Distal
- At the radial tuberosity of the elbow. “pop” felt at the elbow when the tendon ruptures. Rupture must be repaired otherwise there will be loss of flexion and supination.
- Hook test: The patient actively supinates and flexes the elbow at 90 degrees. If the distal biceps tendon can be hooked form the lateral side of the elbow, then the biceps tendons is intact.
Treatment
- Proximal ruptures can be treated either conservatively or surgically. Non-operatively for elderly and most patients will become asymptomatic after 4-6 weeks. Includes rest, ice and physical therapy.
- Surgical treatments is reattaching the torn section of the tendon to the bone (tenodesis). It is usually done in association with other reconstructive surgery. Rarely done for cosmesis.
- Avulsion of the distal biceps tendon is treated with tenodesis using sutures to anchor the tendon into the radius.
Biceps tendon subluxation or dislocation
The transverse humeral ligament and pulley system which holds the biceps tendon within the bicipital groove can become injured. leading to subluxation
Great