KIENBOCK DISEASE
• It is the avascular necrosis of the lunate. Lunate is one of the many carpal bones of the hand and wrist.
• Avascular necrosis of the lunate bone usually occurs in males 20-40 years of age.
• Etiology :
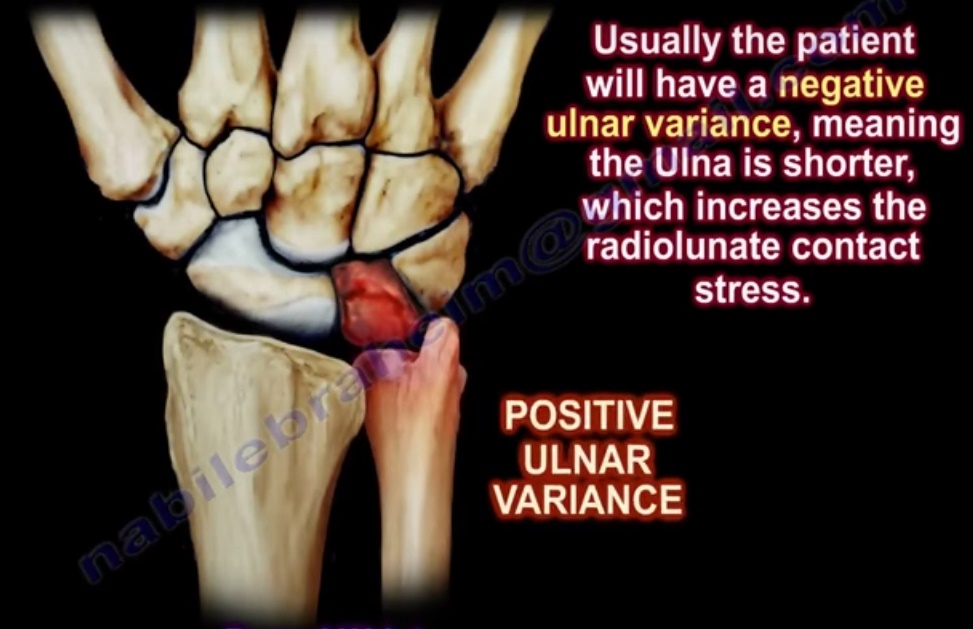
1. Usually the patient will have a negative ulnar variance (ulna is shorter), which increases the radiolunate contact stress
– Normally the distribution of forces across the wrist is 80/20
– But in negative ulnar variance , it becomes 95/5, as ulna is 2.5mm shorter than radius
– And in positive ulnar variance , it becomes 60/40, as ulna is 2.5mm longer than radius
– Ulnar variance is the distance from the radial articular surface to the height of the ulnar head.
– Negative variance increases the shear forces on the lunate.
2. Lunate vascularity variances
– ‘Y’ pattern
– ‘X’ pattern
– ‘I’ pattern(in 31% of patients, has the highest risk of avascular necrosis)
3. Repetitive trauma
– The blood supply of the lunate bone becomes interrupted.
• Initially the condition feels like a wrist sprain, however if it is not recognized and detected early, the condition will progress to collapse of the lunate and arthritis of the wrist.
Clinical presentation
– Activity related
– Insidious onset of pain
– More in the dominant hand
– Decreased ROM and stiffness
– Decreased grip strength
Imaging
1. X-ray wrist- lunate appears white on x-ray, ulna is short (negative ulnar variance). The management would be to shorten the radius, decompress the radius, or revascularize the lunate
2. MRI – for early detection when there is negative ulnar variance and negative x-ray for wrist pain
3. CT scan- it shows the collapse of lunate(seen as lunate necrosis and destruction of the trabeculae).
Classification and concept of treatment
Stage 1 :
X-rays are normal, but changes are seen on the MRI.
Treatment: splint, NSAID medications and rarely surgery
Stage 2:
Sclerosis of the lunate- the bone maintains shape
Treatment: (one of the three ways):
1. Joint leveling procedure- in negative ulnar variance, radial shortening osteotomy is done. And in positive or neutral ulnar variance- capitate shortening is done.
2. Distal radius core decompression incites a local vascularization healing in the lunate.
3. Revascularization procedure.
Stage 3a:
The lunate begins to collapse with no scaphoid rotation
Treat as stage 2
Stage 3b:
The lunate has collapsed with fixed scaphoid rotation
Treatment: Proximal row carpectomy (PRC) or STT fusion
Stage 4:
Degenerated adjacent intercarpal joints.
Treatment: Total wrist arthrodesis, Total wrist arthroplasty, ?Proximal row carpectomy
Thank you so much!
Very nice and precise knowledge, thanks