Courtesy: Prof Nabil Ebraheim, University of Toledo, Ohio, USA
Conditions which cause pain and inflammation are treatable with the use of diagnostic and therapeutic injection.
Ankle joint
- The ankle joint is formed by the articulation of the tibia and talus.
- Injection is done to alleviate pain occurring from trauma, arthritis, gout or other inflammatory conditions.
Anterolateral ankle impingement
- Can occur due to the build-up of scar tissue in the ankle joint or from the presence of bony spurs
- With the ankle in a neutral position, mark the injection site just above the talus and medial to the tibialis anterior tendon.
- The injection site is disinfected with betadine. •The needle is inserted into the identified site and directed posterolaterally. •Injection of the solution into the joint space should flow smoothly without resistance. •Pulling on the foot to distract the ankle joint is helpful.
First metatarsophalangeal joint
- The MTP joint is a common injection site frequently affected by gout and osteoarthritis.
- The injection site is disinfected with betadine.
- The needle is inserted on the dorsomedial or dorsolateral surface.
- The needle is angled to 60-70 degrees to the plane of the match the slope of the joint.
- Injection of the solution into the joint space should flow smoothly without resistance. •Pulling on the big toe is sometimes helpful in distraction of the joint.
Peroneal tendonitis
- Peroneal tendonitis is an irritation to the tendons that run on the outside area of the ankle, the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis.
- The injection site is disinfected with betadine
- Insert the needle carefully in a proximal direction when injecting the peroneus brevis and longus tendon sheath.
- Advance the needle distally to inject the peroneus brevis alone at its bony insertion. Achilles tendonitis
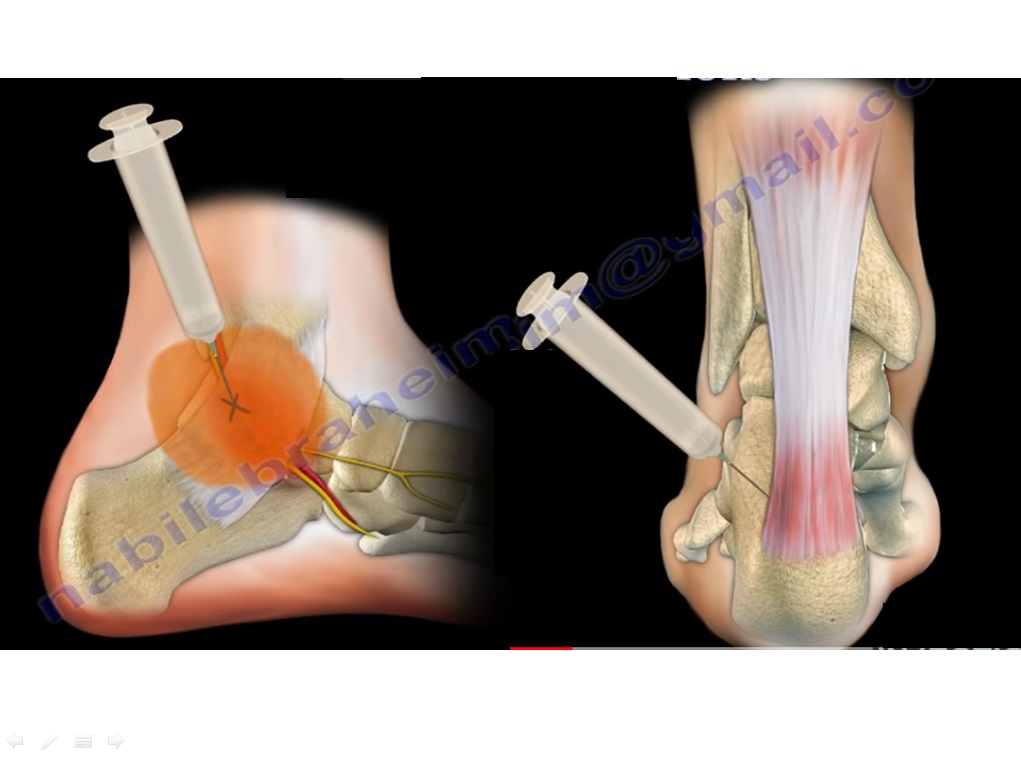
Achilles tendonitis is irritation and inflammation of the large tendon in the back of the ankle.
- Achilles tendonitis is a common overuse injury that occurs in athletes.
- Injection of steroid should be given around the tendon, not through the tendon.
- Injections directly into the tendon is not recommended due to increased risk of tendon rupture.
- Platelets injection can be done through the tendon with needling and fenestration.
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
- The condition of pain and paresthesia caused by irritation to the posterior tibial nerve.
- Feel the pulse of the posterior tibial artery, the nerve is posterior, find the area of maximum tenderness, 1-2 cm above it will be the injection site that is marked on the medial side of the foot and disinfected with betadine.
- The solution is injected at an angle of 30 degrees and directed distally. •Warn the patient that the foot may become numb.
- Care should be taken In walking an driving.
- Usually performed after a treatment program which can include rest, stretching and the use of shoe inserts.
Plantar fasciitis
- The plantar fascia is a band of connective tissue deep to the fat pad on the plantar aspect of the foot.
- Patients with plantar fascia complain of chronic pain symptoms that are often worse in the morning with walking.
- The injection site is identified and marked on the medial side of the foot and betadine used.
- Avoid injecting through the fat pad at the bottom of the foot to avoid fat atrophy.
- The needle is inserted in a medial to lateral direction one finger breathe above the sole of the foot in a line that corresponds to the posterior aspect of the tibia.
- The solution is injected past the midline of the width of the foot.
Leave a Reply